The Astrophysics Projects Division (ApPD) at Goddard Space Flight Center explores some of the most fundamental questions regarding the origins, fate, and the physical forces and laws of the universe. ApPD's objective is to ensure the success of pre-formulation activities for current and future astrophysics missions such as the Habitable Worlds Observatory Technology Maturation Project Office, the Advanced Telescope for High-Energy Astrophysics (ATHENA), the Ultraviolet Transient Astronomy Satellite (ULTRASAT), and the Fornax Initiative. ApPD also oversees all space science missions in operations, including flagships such as the Hubble Space Telescope, the James Webb Space Telescope, and all missions currently being operated by the Space Science Mission Operations project.
Physics of the Cosmos/Cosmic Origins Program Office
The Physics of the Cosmos (PhysCOS) and Cosmic Origins (COR) Program Office at Goddard Space Flight Center, along with the Exoplanet Exploration Program (ExEP) at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), was established by NASA’s Astrophysics Division to understand the three most fundamental questions related to astrophysics: “How did we get here?” (COR), “How does the universe work?” (PhysCOS), and “Are we alone?” (ExEP). The PhysCOS/COR Program Office includes early mission initiatives directed by NASA Headquarters before assignment to a center, such as the Time Domain Astronomy/Multi-Messenger Astrophysics (TDAMM) Initiative and the Astrophysics Cross Observatory Science Support (ACROSS) pilot project, as well as science community coordination and Strategic Astrophysics Technology support in managing competed and directed PhysCOS-and-COR-related strategic technologies.
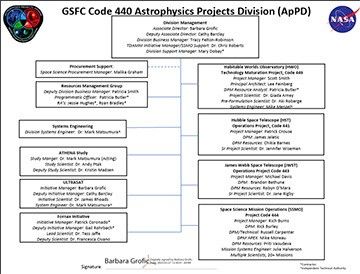
Organization
Flight Projects























-Carolyn_Y._Ng.jpeg?w=1024)




