PhysCOS and COR Strategic Technology Portfolio
For more information about these technologies visit our Technology Database.

Mechanical engineering meta-shell test with aluminum structural shell, 54 glass test segments, 216 spacers, and 432 epoxy bonds
Significance: World-class thin grazing-angle X-ray mirror technology; baselined for Lynx Xray flagship mission concept
Project Title: High-Resolution and Lightweight X-ray Optics for the X-ray Surveyor
PI: Zhang, William (GSFC)
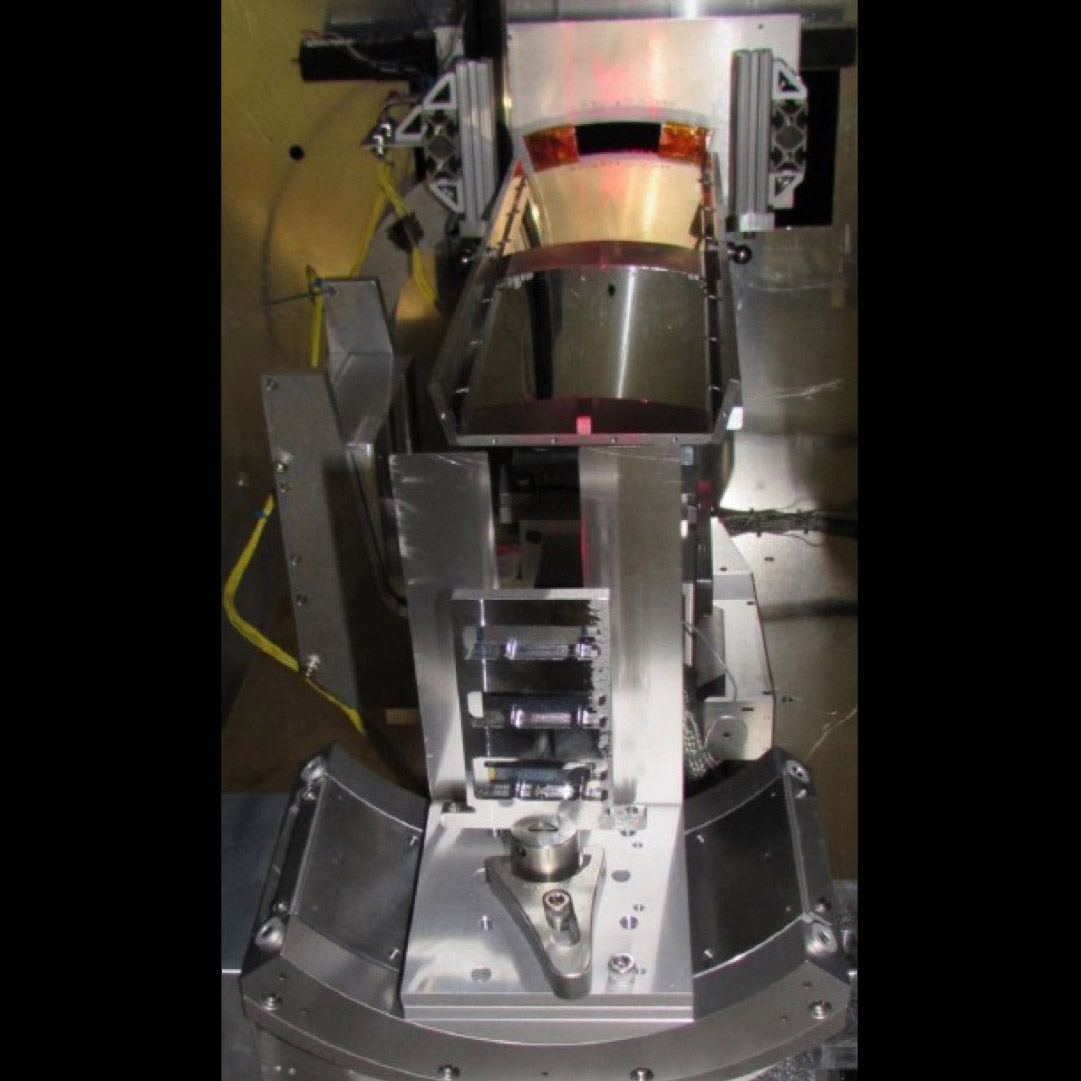
X-ray Critical-Angle Transmission (CAT) gratings during optical alignment
Significance: Highest-resolution X-ray grating technology; baselined for Lynx X-ray flagship mission concept
Project Title: Development of a CAT Grating Spectrometer
PI:Mark Schattenburg (MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research)
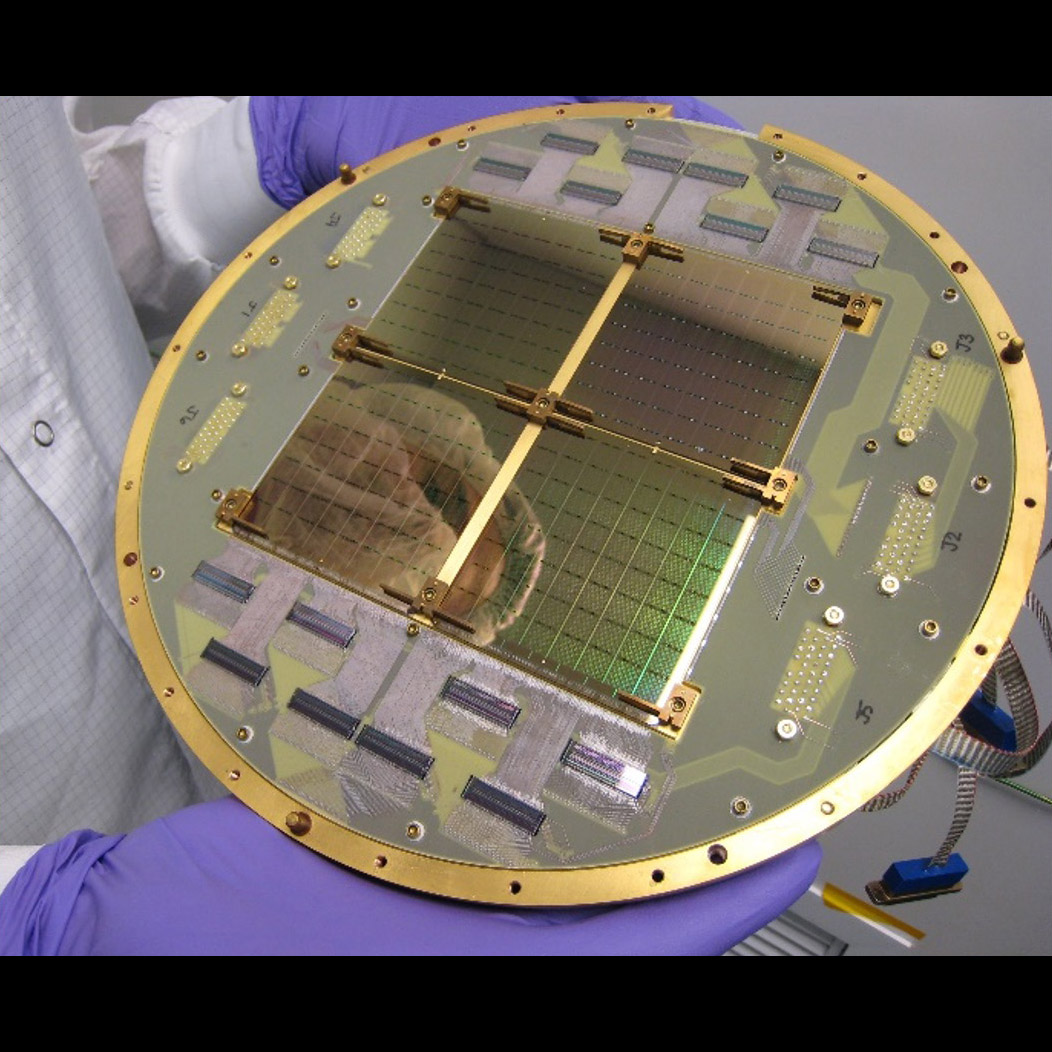
Large-format antenna-coupled bolometer arrays for Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) polarimetry
Significance: Developing antenna designs providing sensitivity, stability, and minimized particle susceptibility for bands required by the Inflation Probe, enabling identification of Inflation instants after the Big Bang
Project Title: Planar Antenna-Coupled Superconducting Detectors for CMB Polarimetry
PI: James Bock (JPL/Caltech)
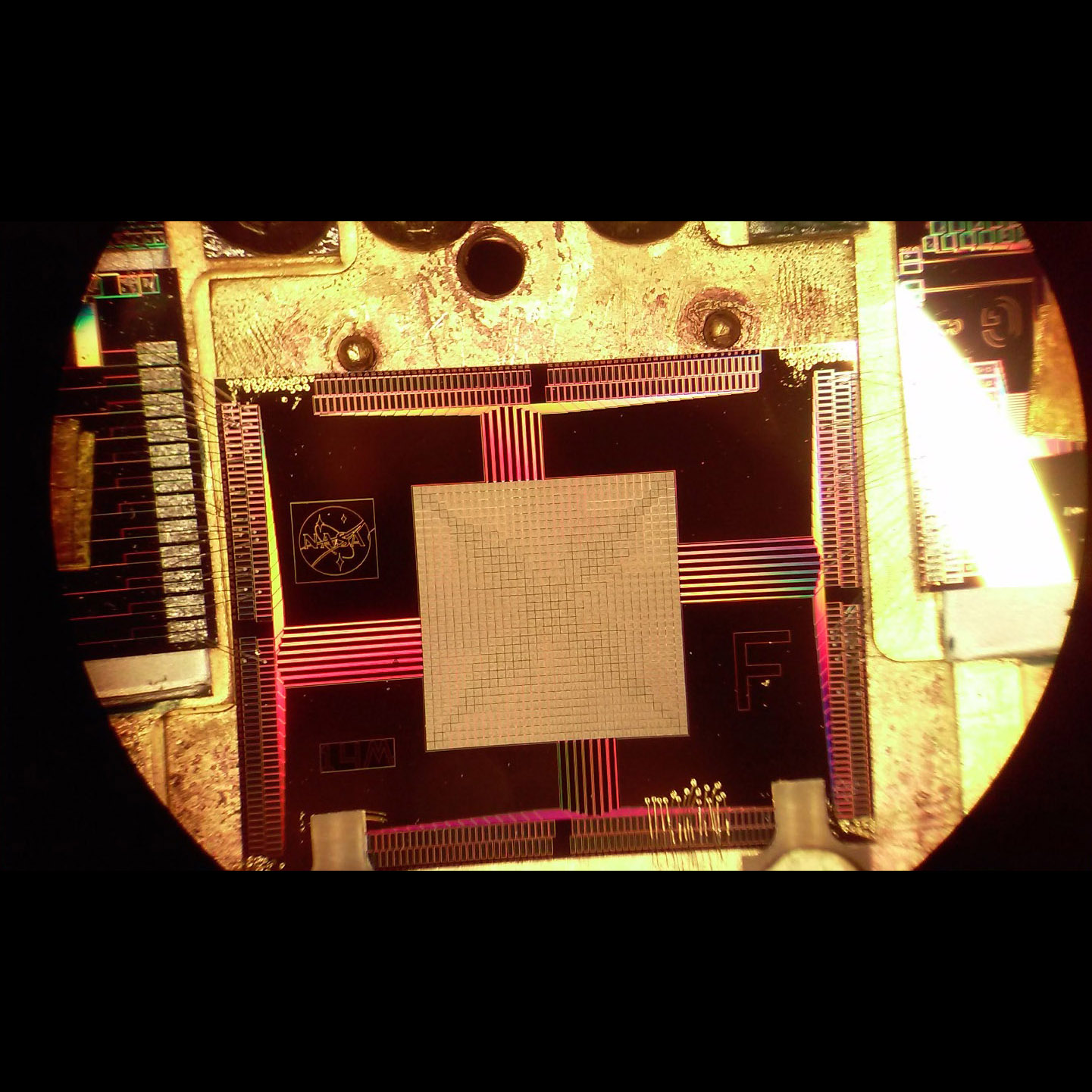
Candidate demonstration model Transition-Edge Sensors (TESs) array for the ATHENA X-ray Integral Field Unit (X-IFU)
Significance: TES microcalorimeters offer energy resolution for the European ATHENA mission
Project Title: Providing enabling and enhancing technologies for a demonstration model of the ATHENA X-IFU
PI: Caroline Kilbourne (GSFC)
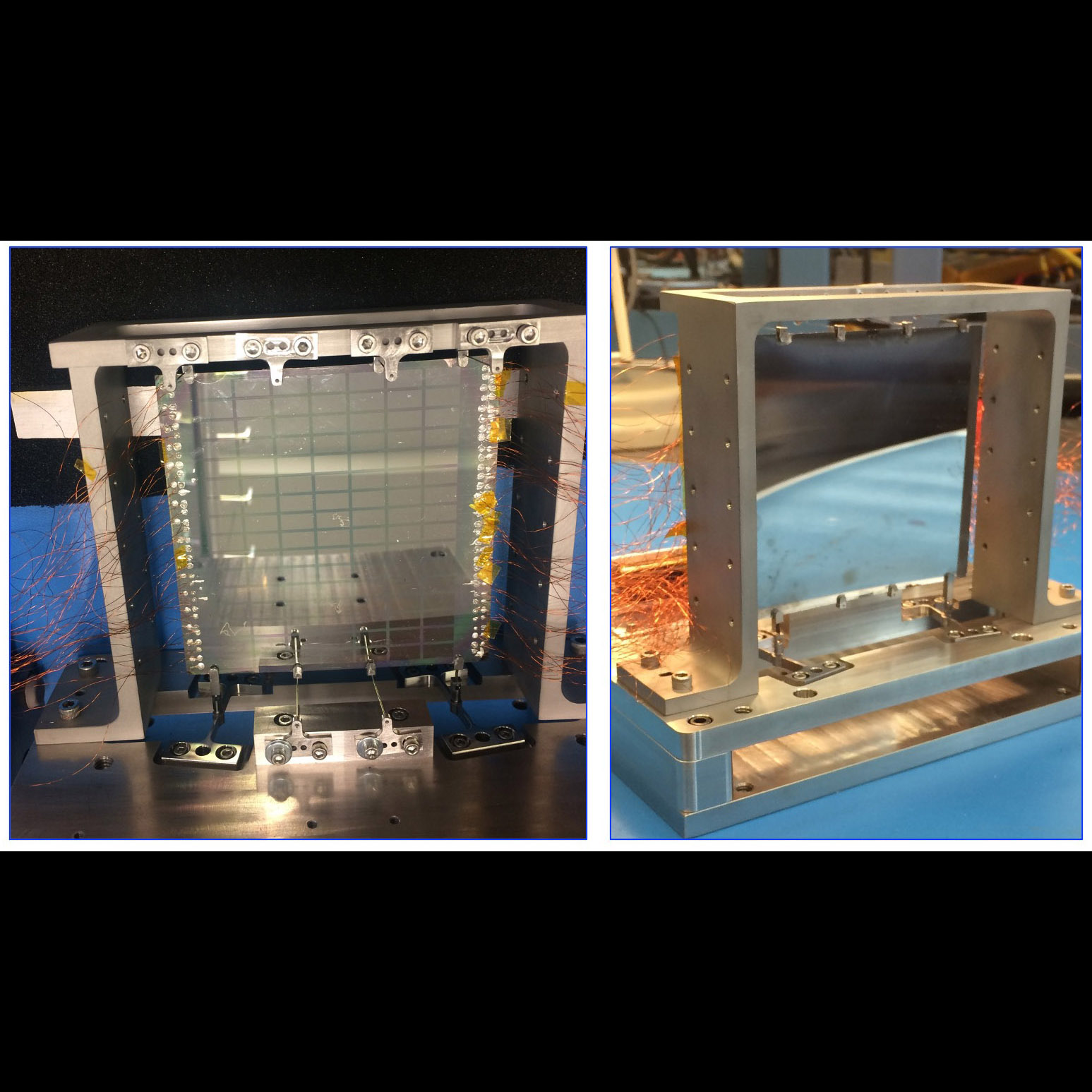
Mounted adjustable cylindrical X-ray mirror showing piezo cells and wiring
Significance: Adjustable X-ray optics are a backup technology for the Lynx large mission concept
Project Title: Development of 0.5-Arc-second Adjustable Grazing-Incidence X-ray Mirrors for
the SMART-X Mission Concept
PI: Paul Reid (SAO)

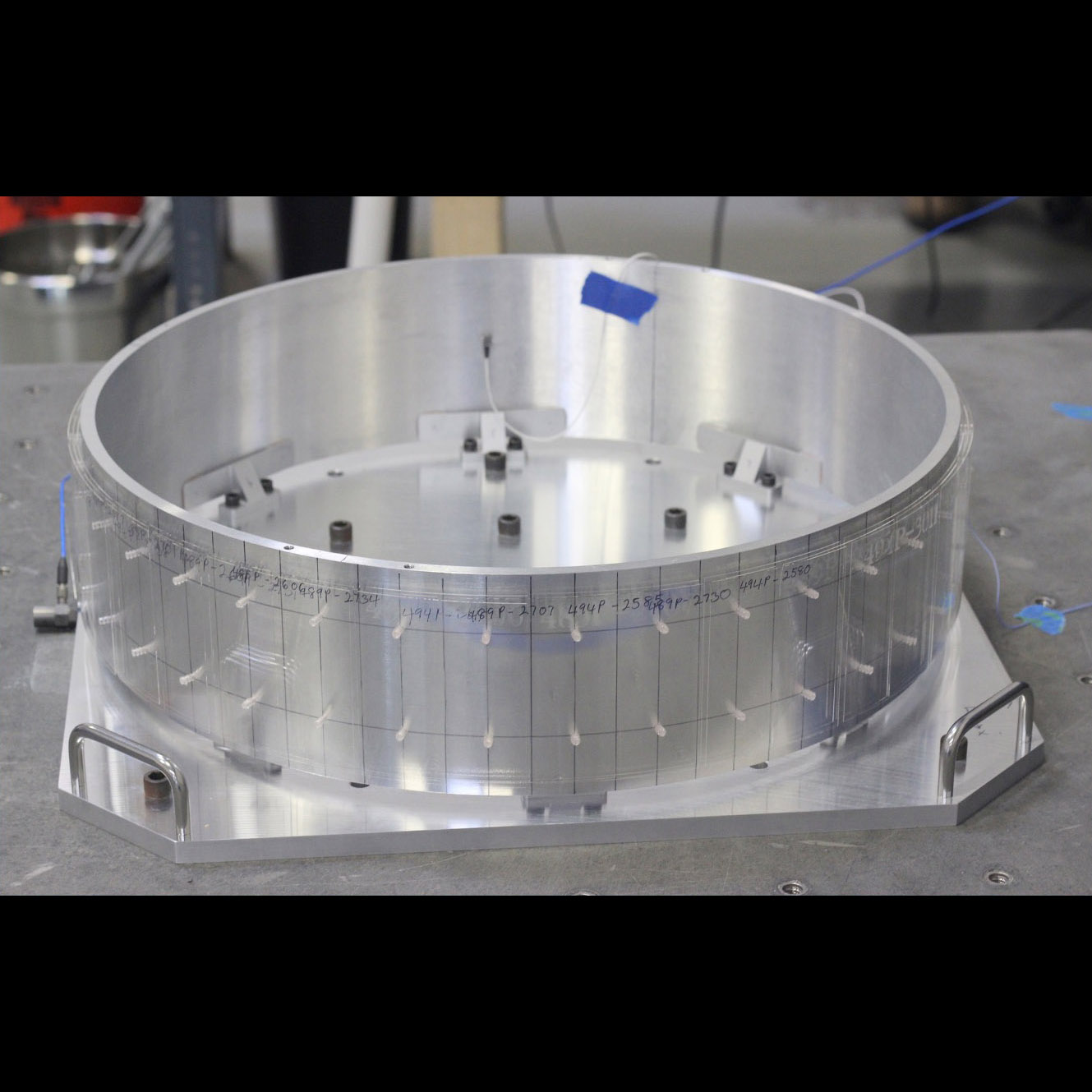
Students working on REXIS, a student-built instrument deployed on the OSIRIS-REx mission to Asteroid Bennu, that deployed with directly deposited filter on its X-ray CCDs
Significance: X-ray detectors operate far better when filters allow X-ray photons through and block longer wavelength light
Project Title: Directly-Deposited Blocking Filters for X-ray Imaging Detectors
PI: Mark Bautz (MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research)
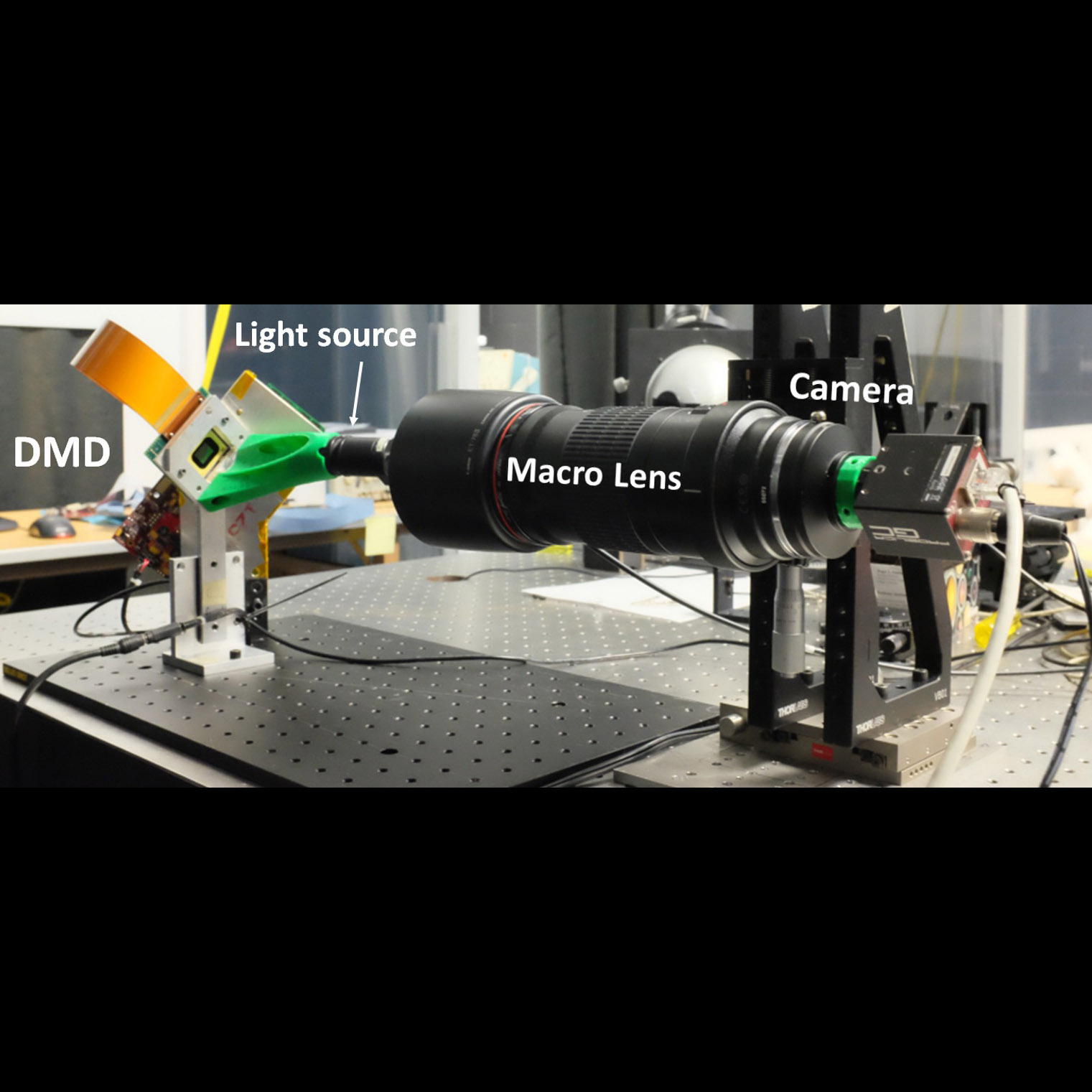

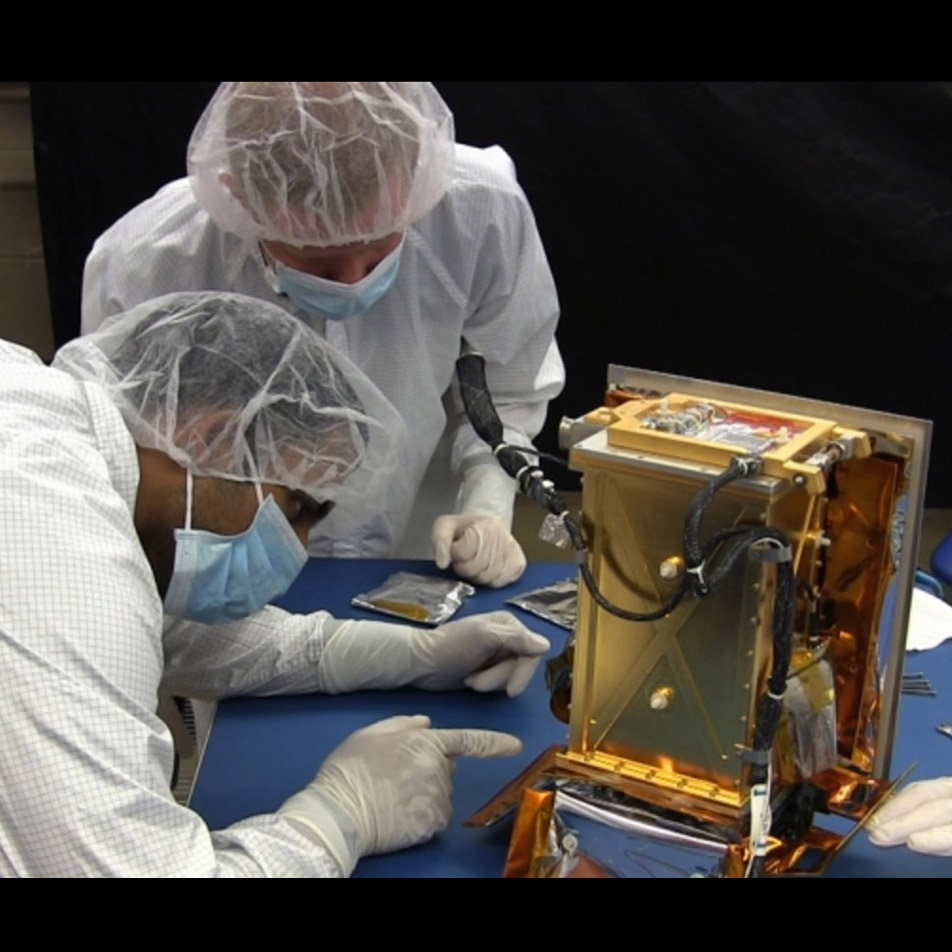
Detecting tripped micro-mirrors in Digital Micro-mirror Device (DMD) during vibration and shock testing done as part of flight qualification
Significance:Replacing windows of commercially available DMDs may enable far-UV multiobject spectrometry in future missions
Project Title: Development of DMDs for Far-UV Applications
PI: : Zoran Ninkov (RIT)
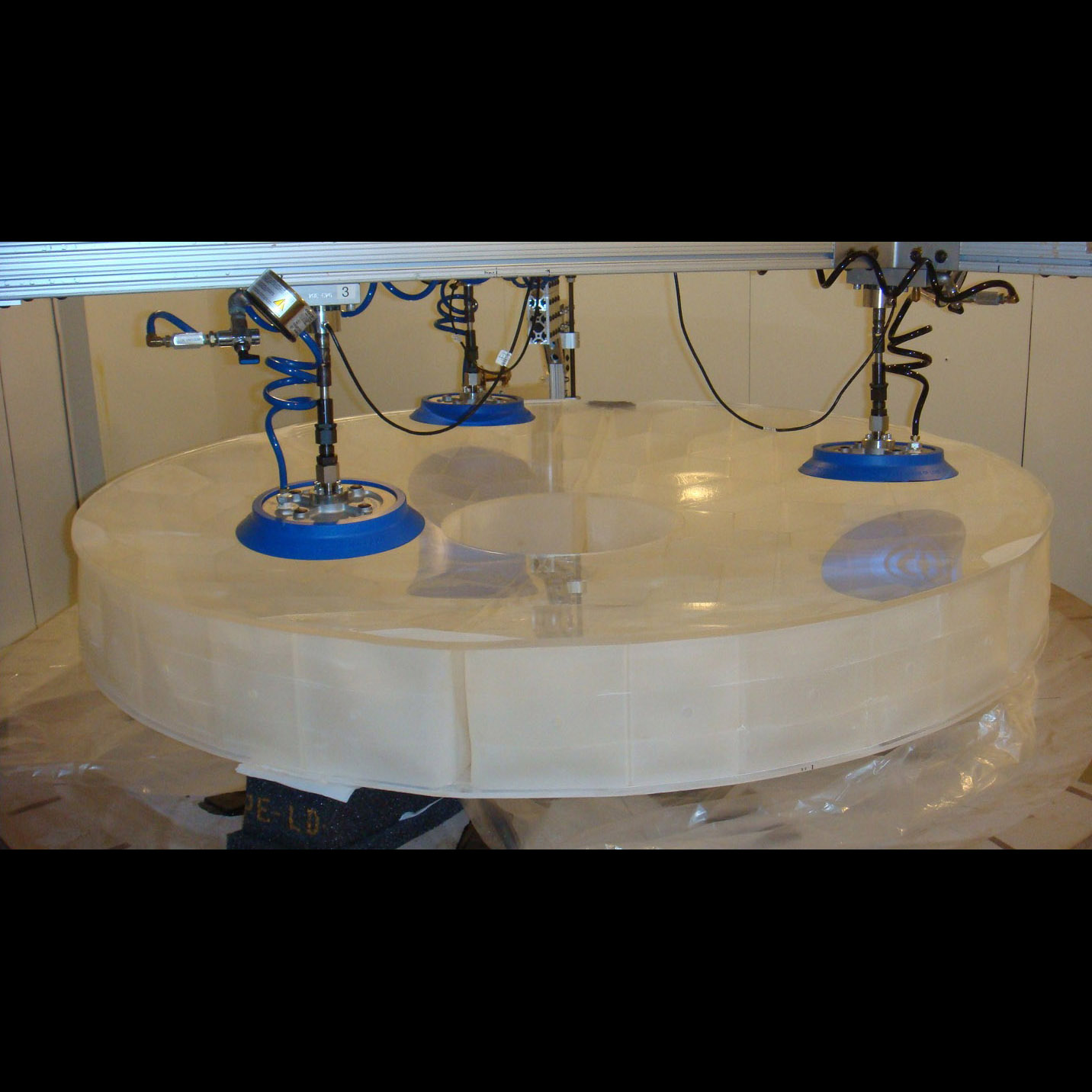

1.5-m mirror blank after grinding and polishing
Significance: Deep-core manufacturing enables 4-m-class mirrors such as planned for the HabEx exoplanet observatory concept with significantly lower cost and risk
Project Title: Advanced Mirror Technology Development (AMTD) for Very Large Space Telescopes
PI: H. Philip Stahl (MSFC)
1.5-m mirror with strip heaters placed at 120⁰ intervals on its outside, and 18 thermocouples on its back and sides, as well as measuring the ambient temperature
Significance:This technology may enable required ultra-stability (~10 pm) for HabEx and LUVOIR missions
Project Title: Predictive Thermal Control (PTC) Technology to enable Thermally Stable Telescopes
PI: H. Philip Stahl (MSFC)

Delta-doped Electron-Multiplied CCD detectors (EMCCD) deployed at Palomar
Significance: Advanced detectors developed by this project are baselined by SHIELDS, HabEx, LUVOIR, and ground
facilities
Project Title: Advanced FUV/UV/Visible Photon-Counting and Ultralow-Noise Detectors
PI: Shouleh Nikzad (JPL/Caltech)
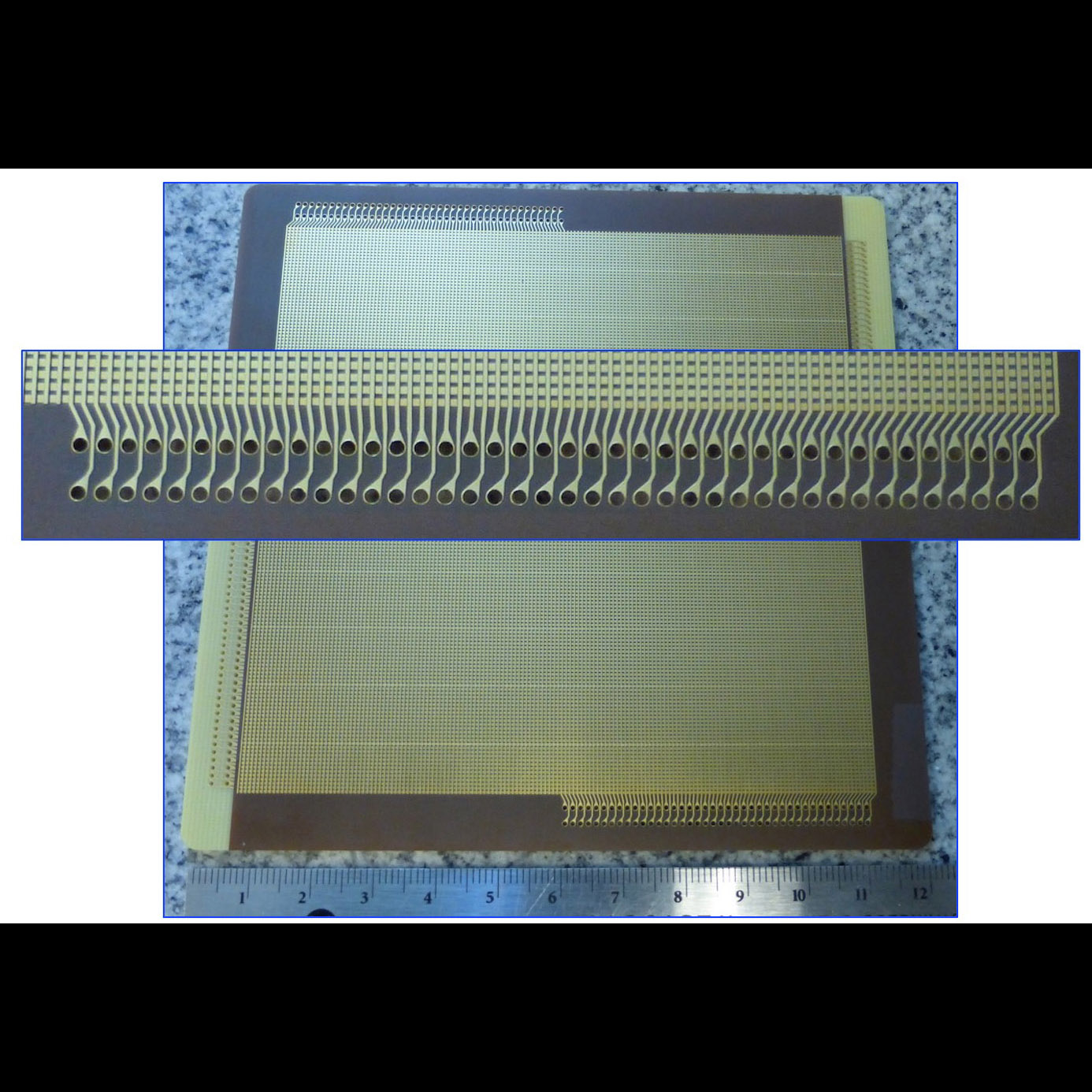

100 mm polyimide anode used for 100×100 mm2 Multi-Channel Plate (MCP) detector
Significance: Large-format low-noise detectors may enable future far-UV missions
Project Title: : Development of 100×100 mm2 photon-counting UV detectors
PI: John Vallerga (UC Berkeley)
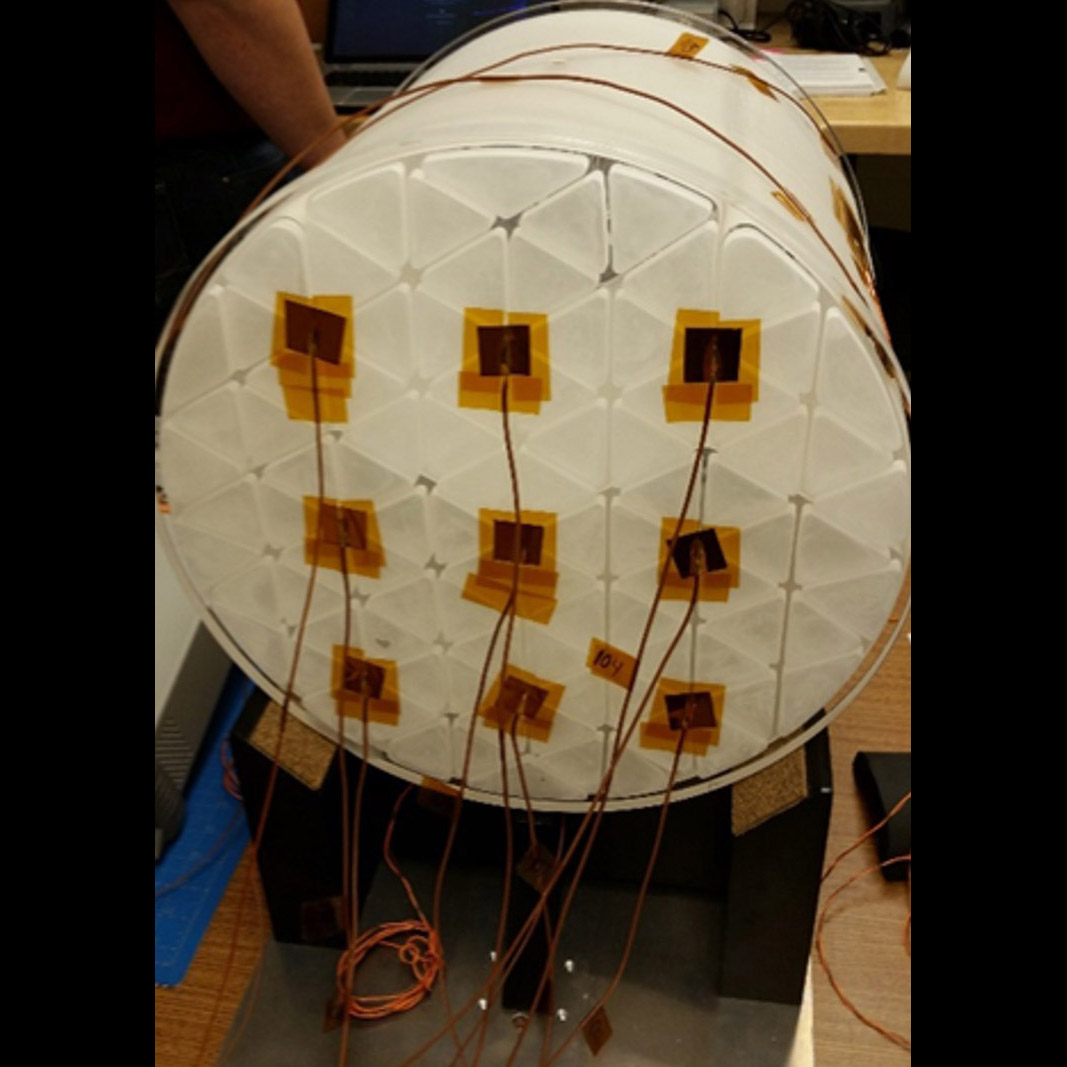
90-GHz feedhorn-coupled focal plane array for performing Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) measurements
Significance: CMB measurements may enable identification of the “Inflation” cosmologists
believe may have occurred instants after the Big Bang
Project Title: High Efficiency Feedhorn-Coupled TES-based Detectors for CMB Polarization
PI: Edward Wollack (GSFC)
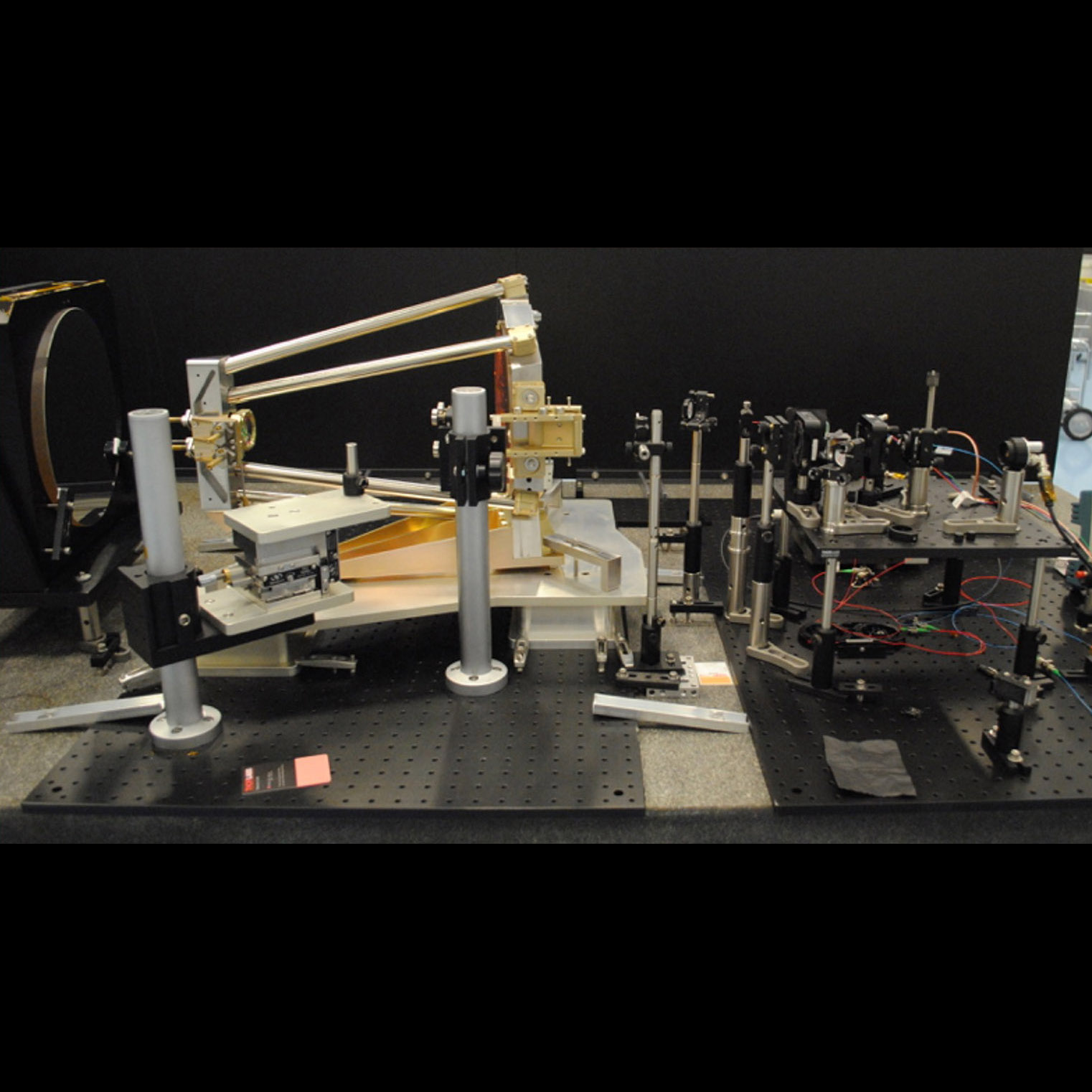
Measuring scattered light in prototype Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) telescope
Significance: The LISA gravitational-wave observatory crucially depends on collecting laser light from a remote spacecraft, millions of km away
Project Title: Telescope Development for the LISA Mission
PI: Jeffrey Livas (GSFC)
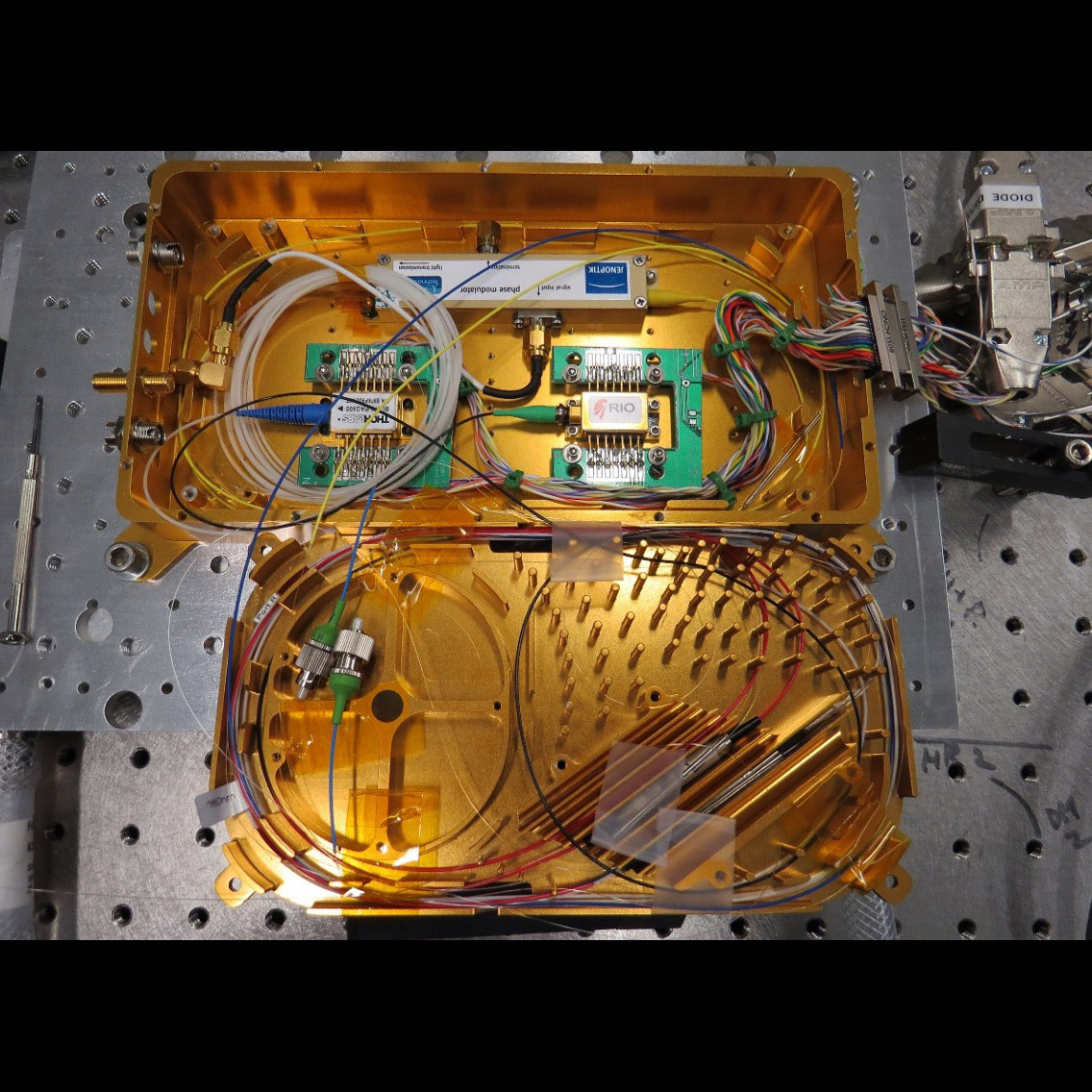
Prototype laser oscillator and pre-amplifier for lasers enabling the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) gravitational-wave observatory
Significance: LISA crucially depends on lasers to allow interferometric measurement of the
multi-million-km distance between the three spacecraft; technology readiness level (TRL) of
5 is needed for infusion into the mission
Project Title: Demonstration of a TRL-5 Laser System for LISA
PI: Jordan Camp (GSFC)
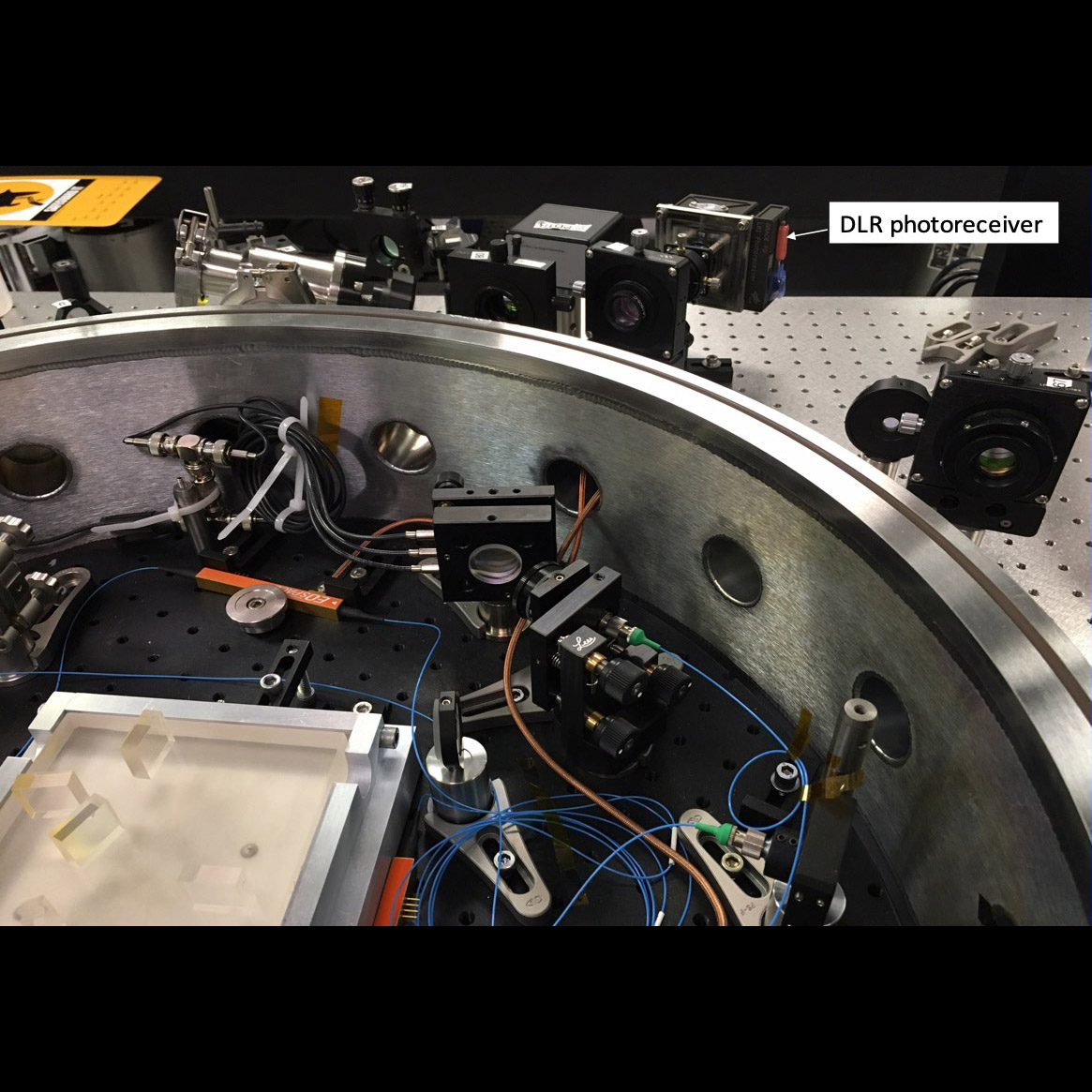
GRACE Follow-On photo-receivers integrated into testbed as part of phasemeter development for the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) gravitational-wave (GW) observatory
Significance: LISA needs a phasemeter system to allow interferometric measurement of the
multi-million-km distance between the three spacecraft
Project Title: Phase Measurement System Development for Interferometric GW Detectors
PI: William Klipstein (JPL)
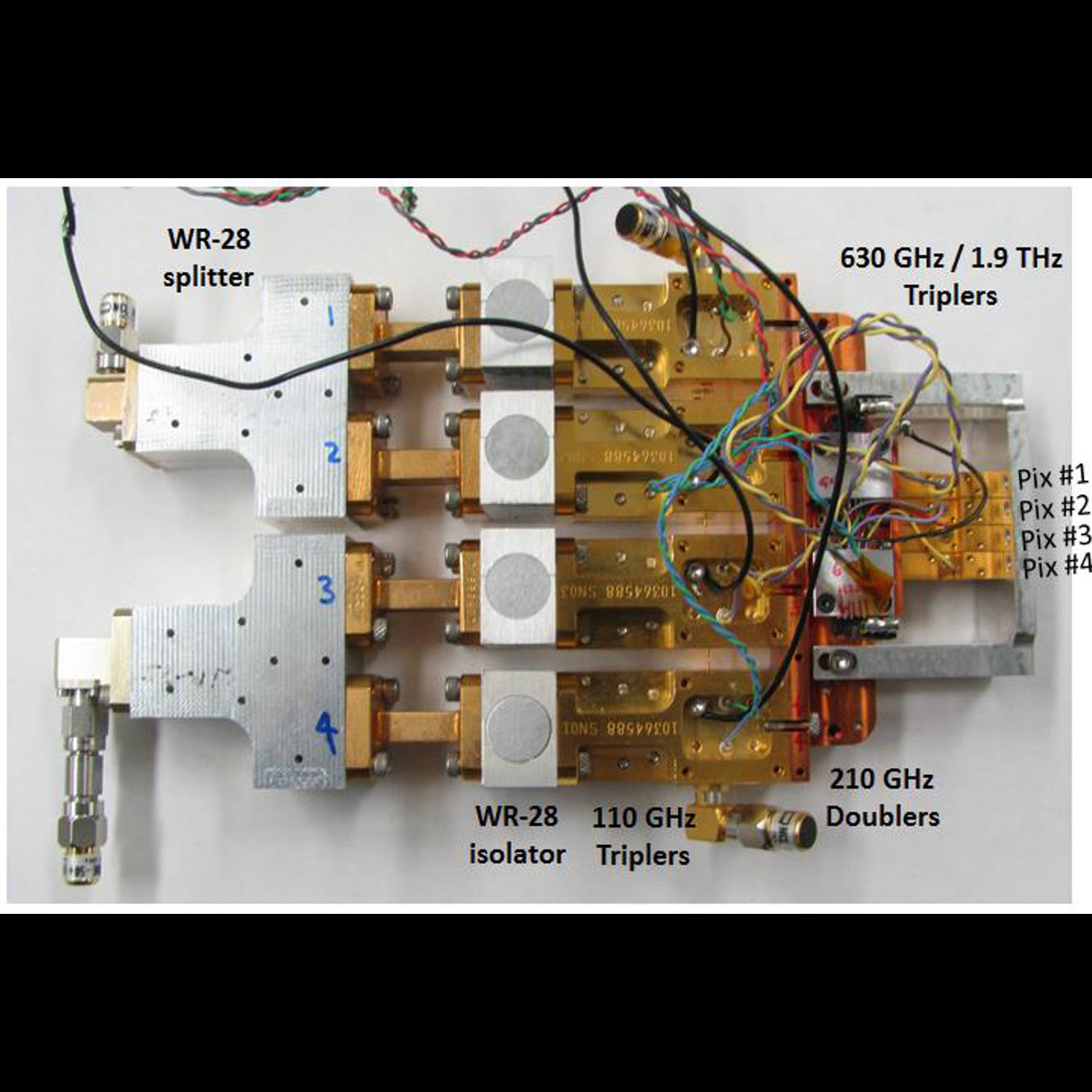
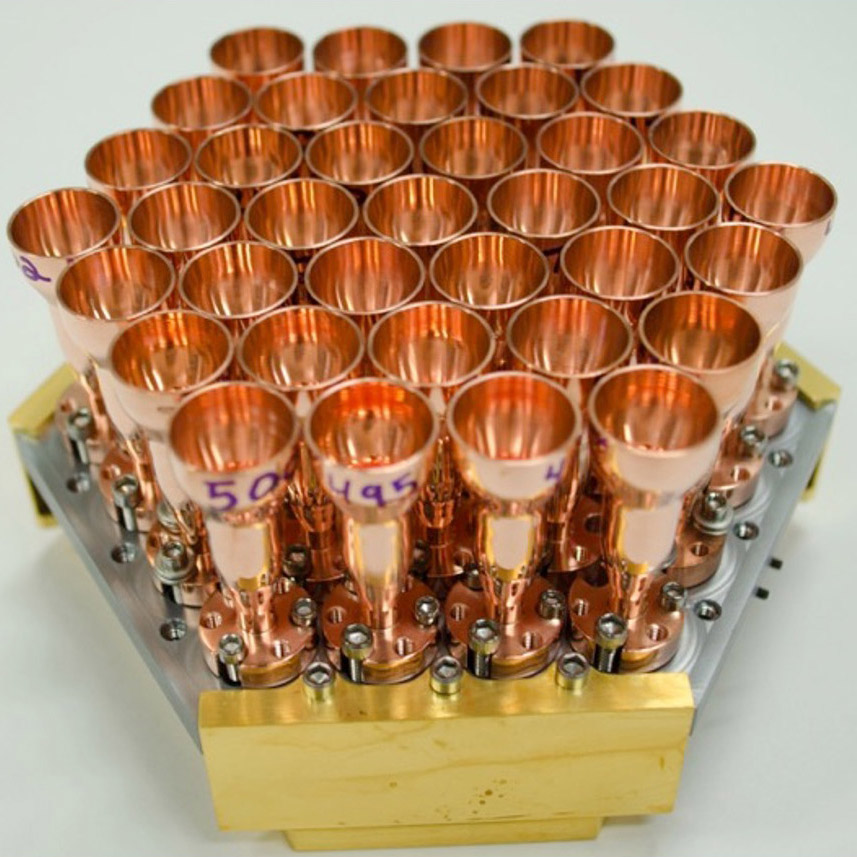
Biasless 1.9-THz triplers developed for multi-pixel Local Oscillator (LO
Significance: This high-resolution multi-pixel far-IR detector technology may enable or enhance future missions
Project Title: A Far-IR Heterodyne Array Receiver for C+ and OI Mapping
PI: Imran Mehdi (JPL)
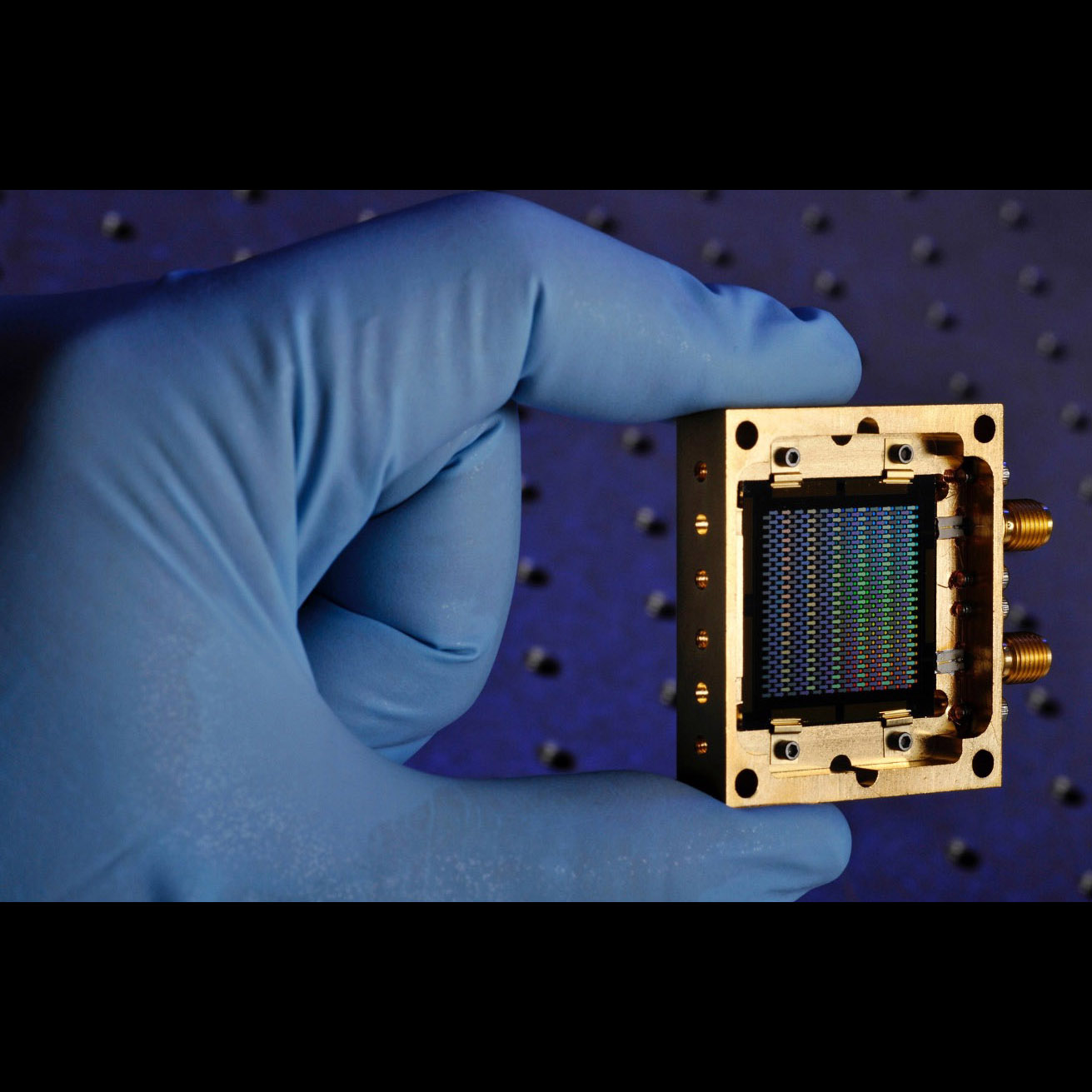
484-pixel 350-mm Kinetic Inductance Detector (KID) array
Significance: Polarization-sensitive arrays in the far-IR can provide critical information
on the role of magnetic fields in galaxy formation and evolution, and star formation in
our galaxy and nearby galaxies
Project Title: KID Imaging Arrays for Far-IR Astrophysics
PI: Jonas Zmuidzinas (JPL)
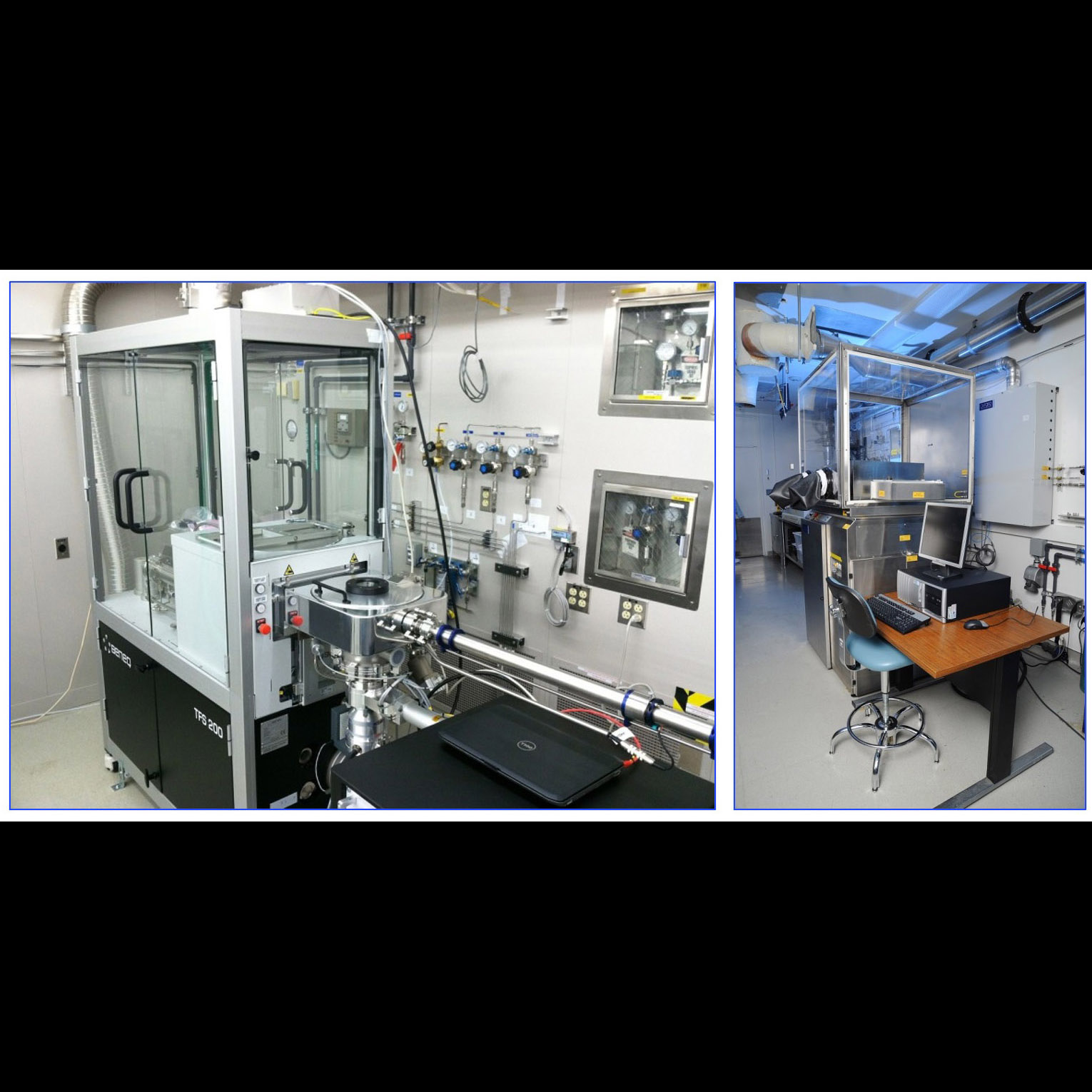

Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) reactors at JPL used for developing advanced UV coatings
Significance:High-reflectivity, high-uniformity, wide-bandpass UV coatings are key for
astrophysics and exoplanet studies
Project Title: UV Coatings, Materials and Processes for Advanced Telescope Optics
PI: Bala K. Balasubramanian (JPL)
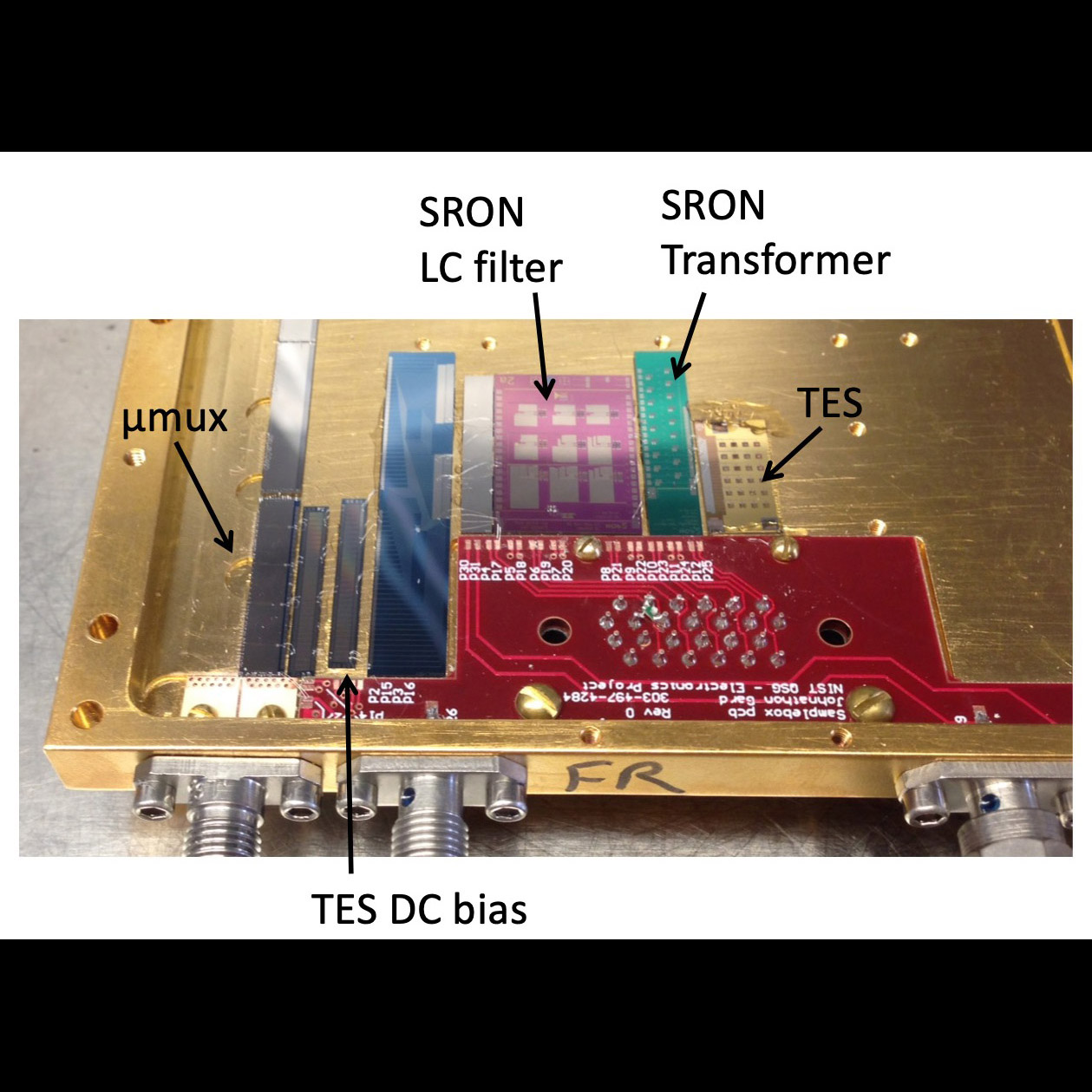
Test box for characterizing AC- and DC-biased Transition-Edge Sensors (TESs)
Significance:: AC-biased TESs and Frequency Division Multiplexing are ATHENA’s baseline
readout architecture
Project Title: Technology Development for an AC-Multiplexed Calorimeter for ATHENA
PI: Joel Ullom (NIST)
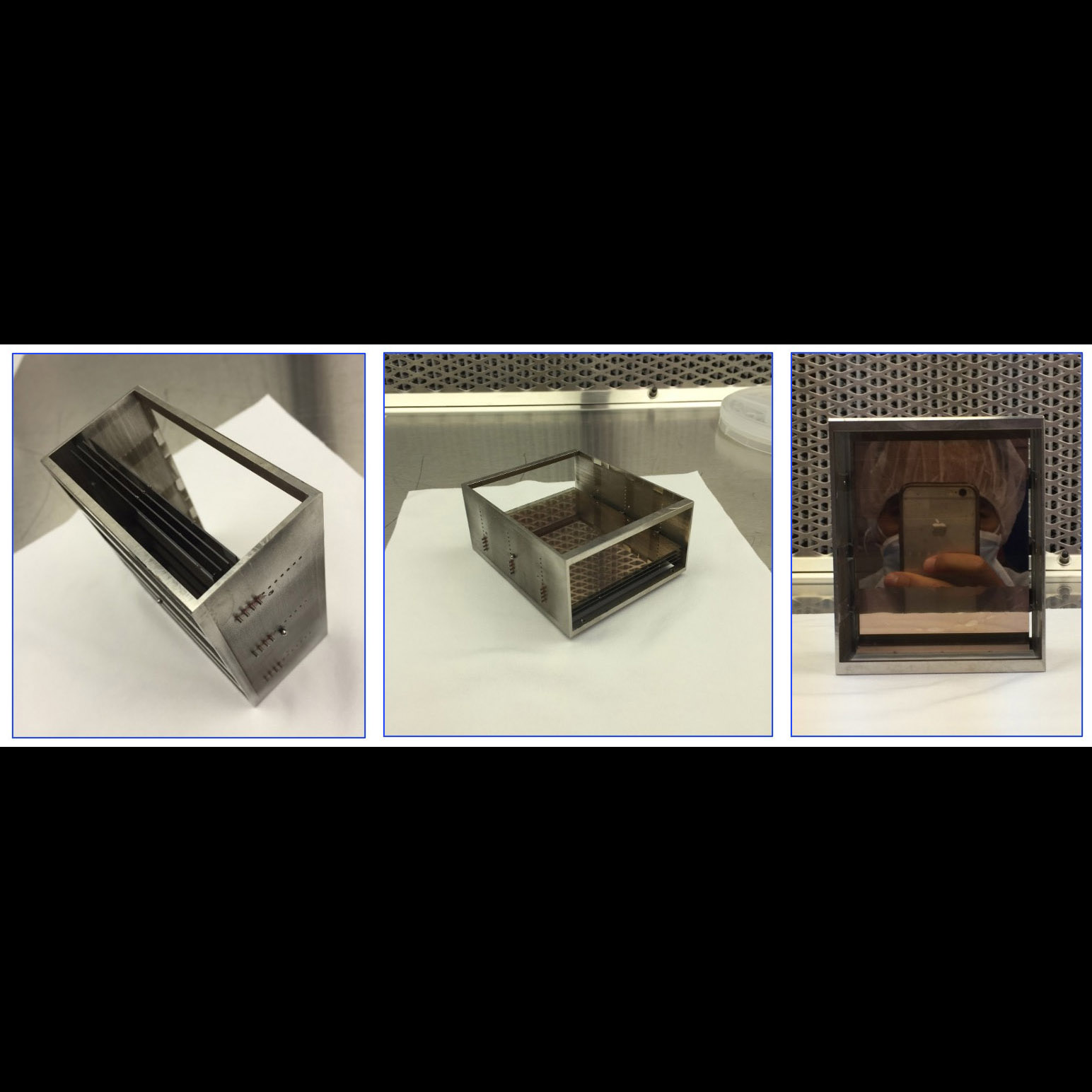
Four X-ray reflection gratings aligned into a single module for testing
Significance: X-ray reflection gratings enable high throughput, high spectral resolving power
below 2 keV, a spectral band holding major astrophysics interest
Project Title: Reflection Grating Modules: Alignment and Testing
PI: Randall McEntaffer (PSU)