Select Gallery View : Slideshow | Thumbnails | PDF

For more information about these technologies visit our Technology Database.
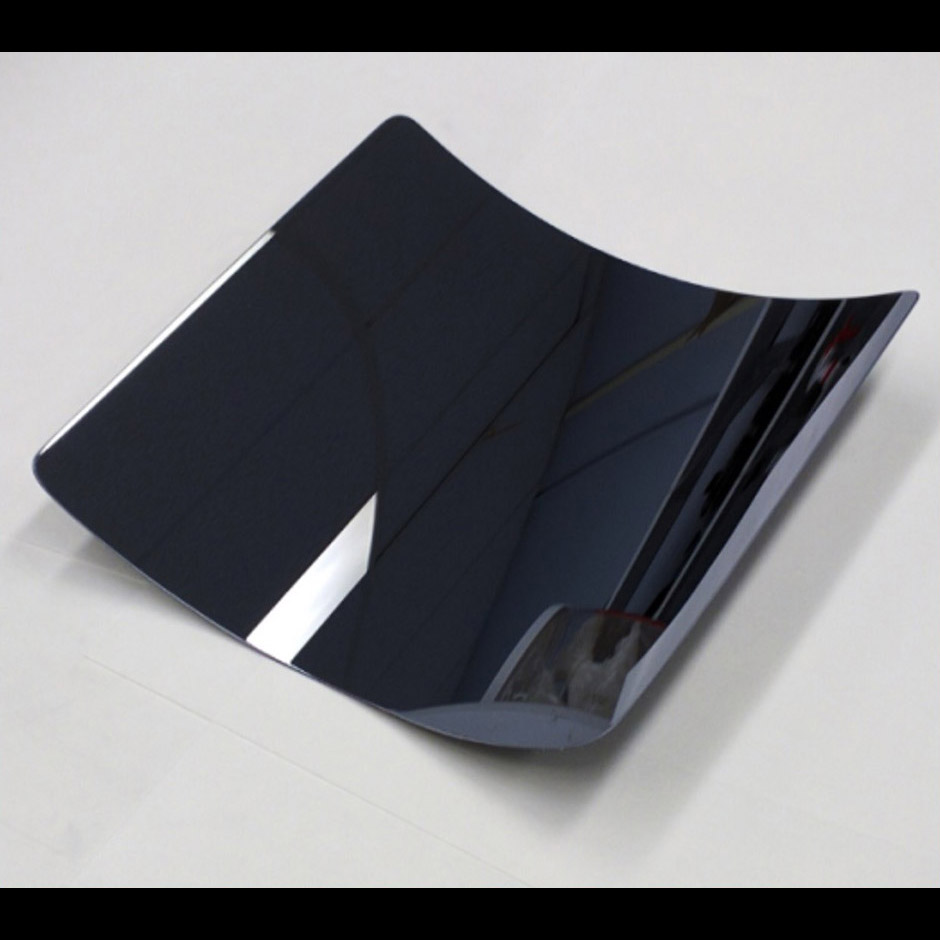


Significance: World-class thin grazing-angle X-ray mirror technology; baselined for Lynx X-ray flagship mission concept
Project Title: Next Generation X-ray Optics: High Resolution, Light Weight, and Low Cost
PI: Zhang, William (GSFC)

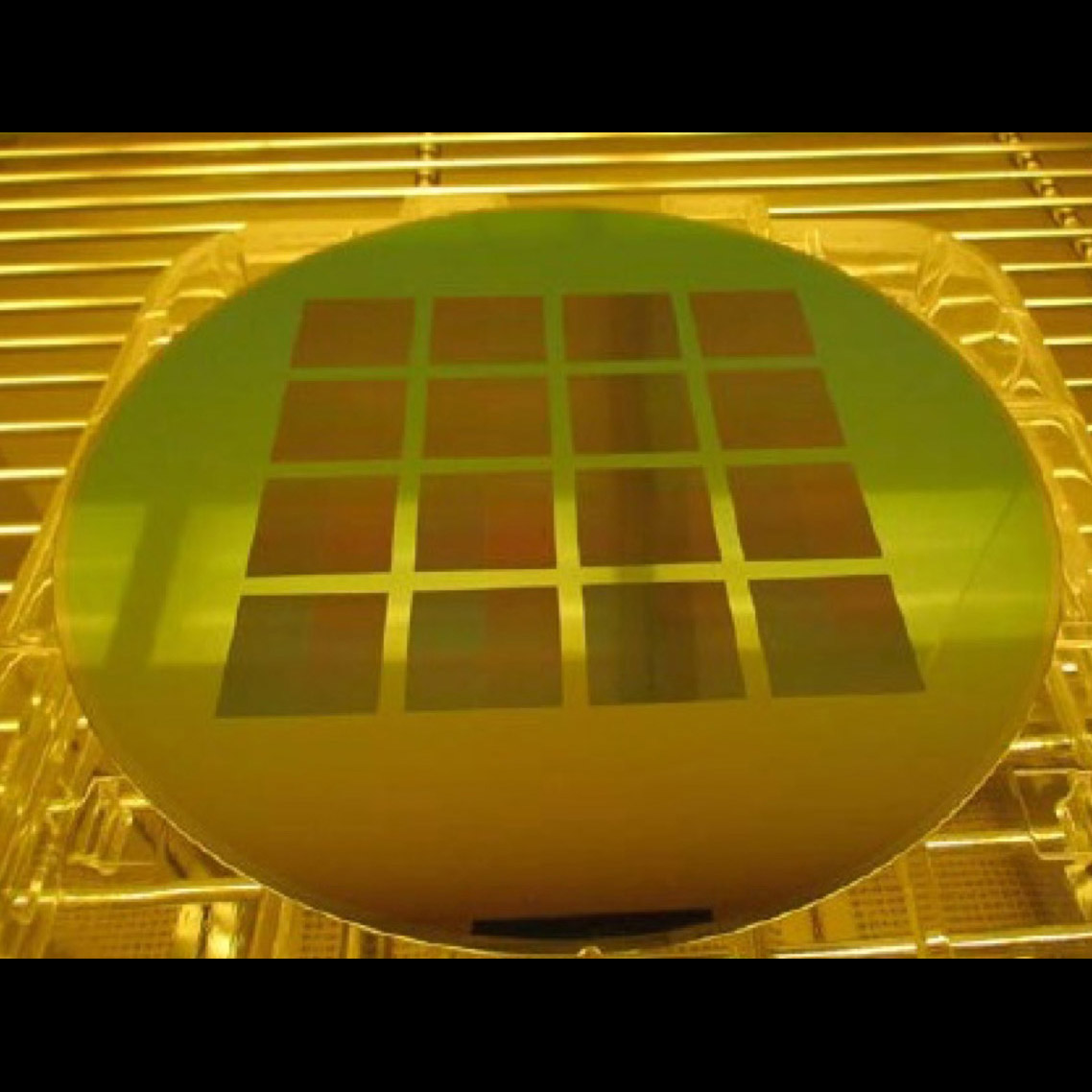
Significance: Highest-resolution X-ray grating technology; baselined for Lynx X-ray flagship mission concept
Project Title: Development of a CAT Grating Spectromete
PI: Mark Schattenburg (MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research)

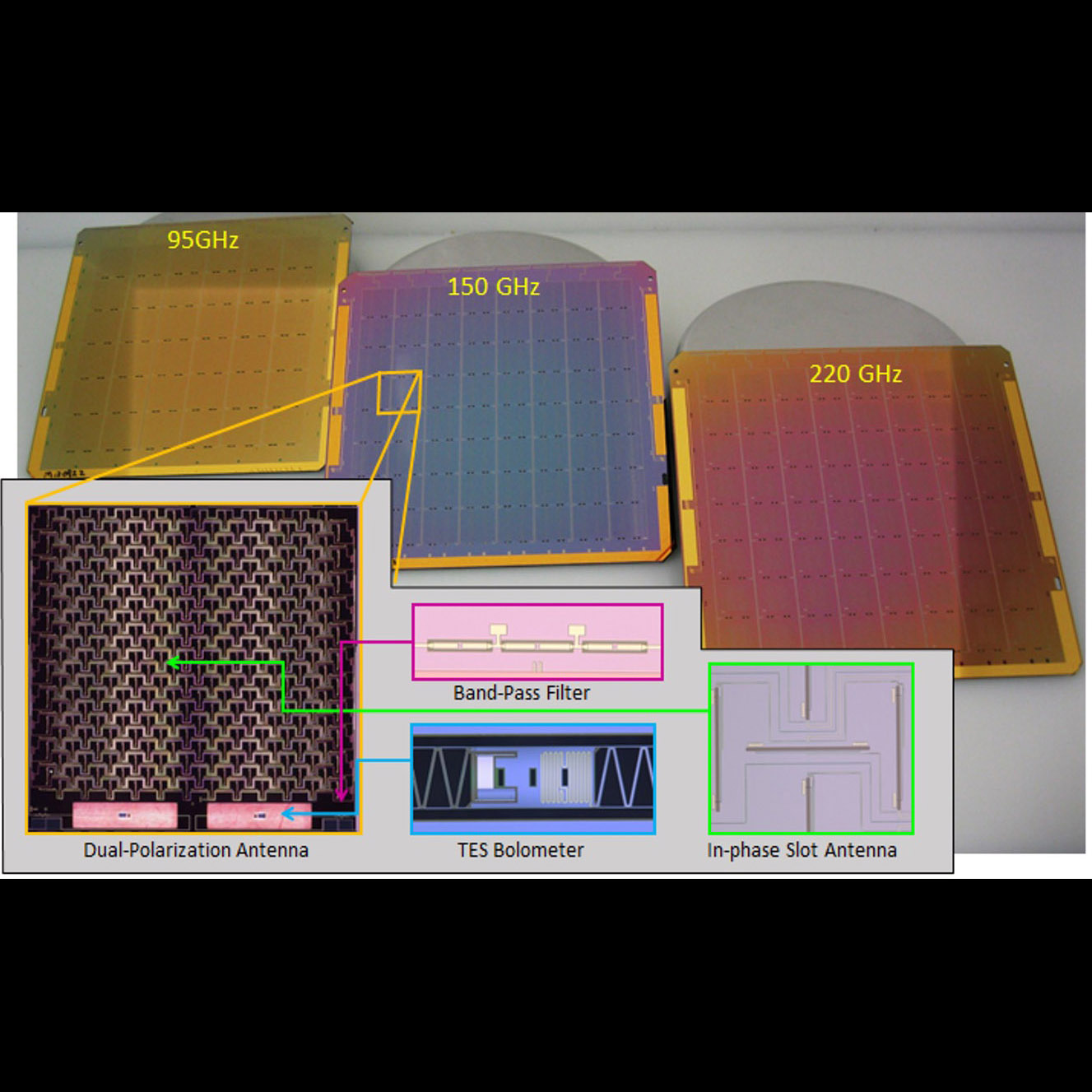
Significance: Developing antenna designs providing sensitivity, stability, and minimized particle susceptibility for bands required by the Inflation Probe, enabling identification of Inflation instants after the Big Bang
Project Title: Planar Antenna-Coupled Superconducting Detectors for CMB Polarimetry
PI: James Bock (JPL/Caltech)

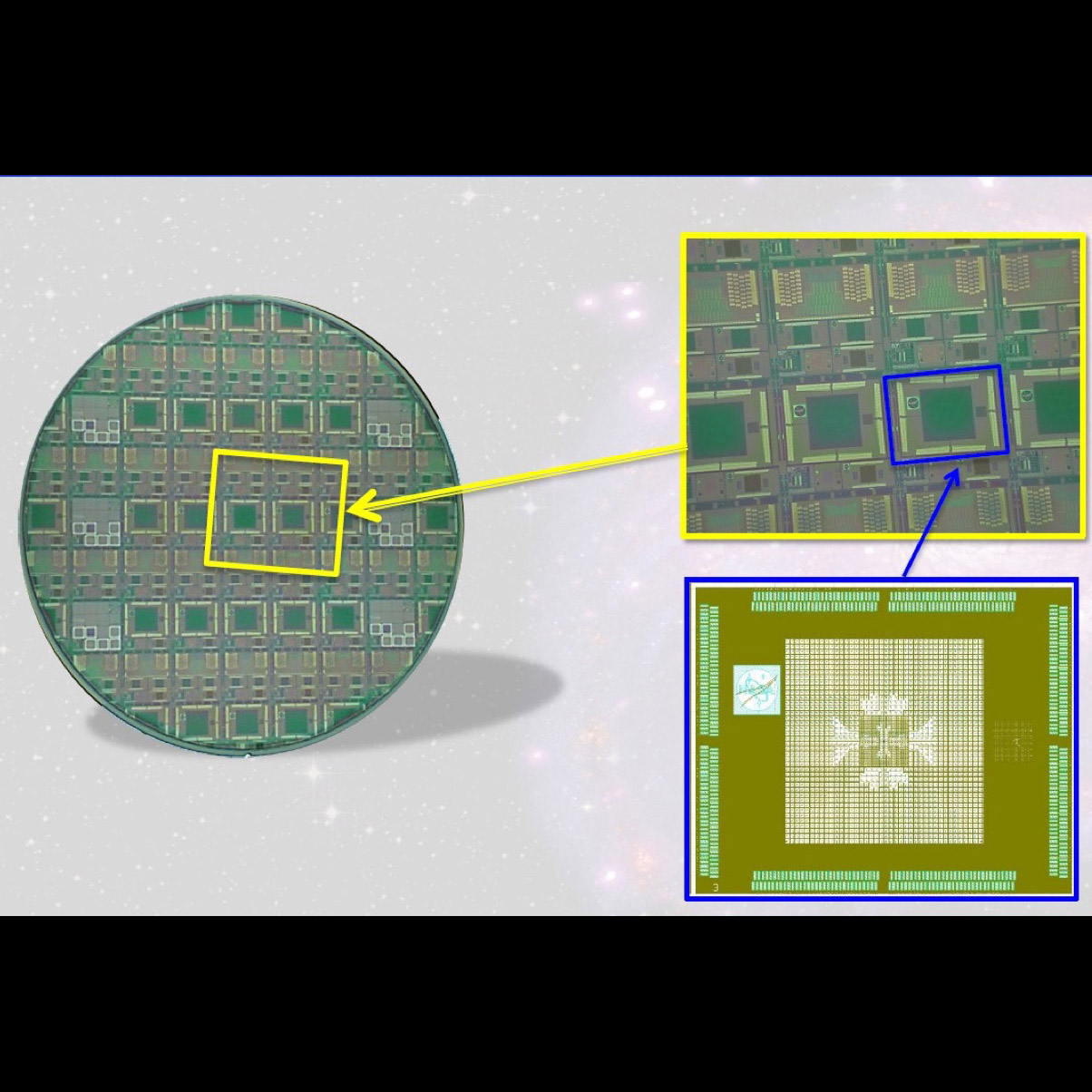
Significance: TES microcalorimeters offer energy resolution that may enable future missions such as the Lynx X-ray flagship mission concept
Project Title: Advanced X-ray Microcalorimeters: TES Microcalorimeters
PI: Caroline Kilbourne (GSFC)

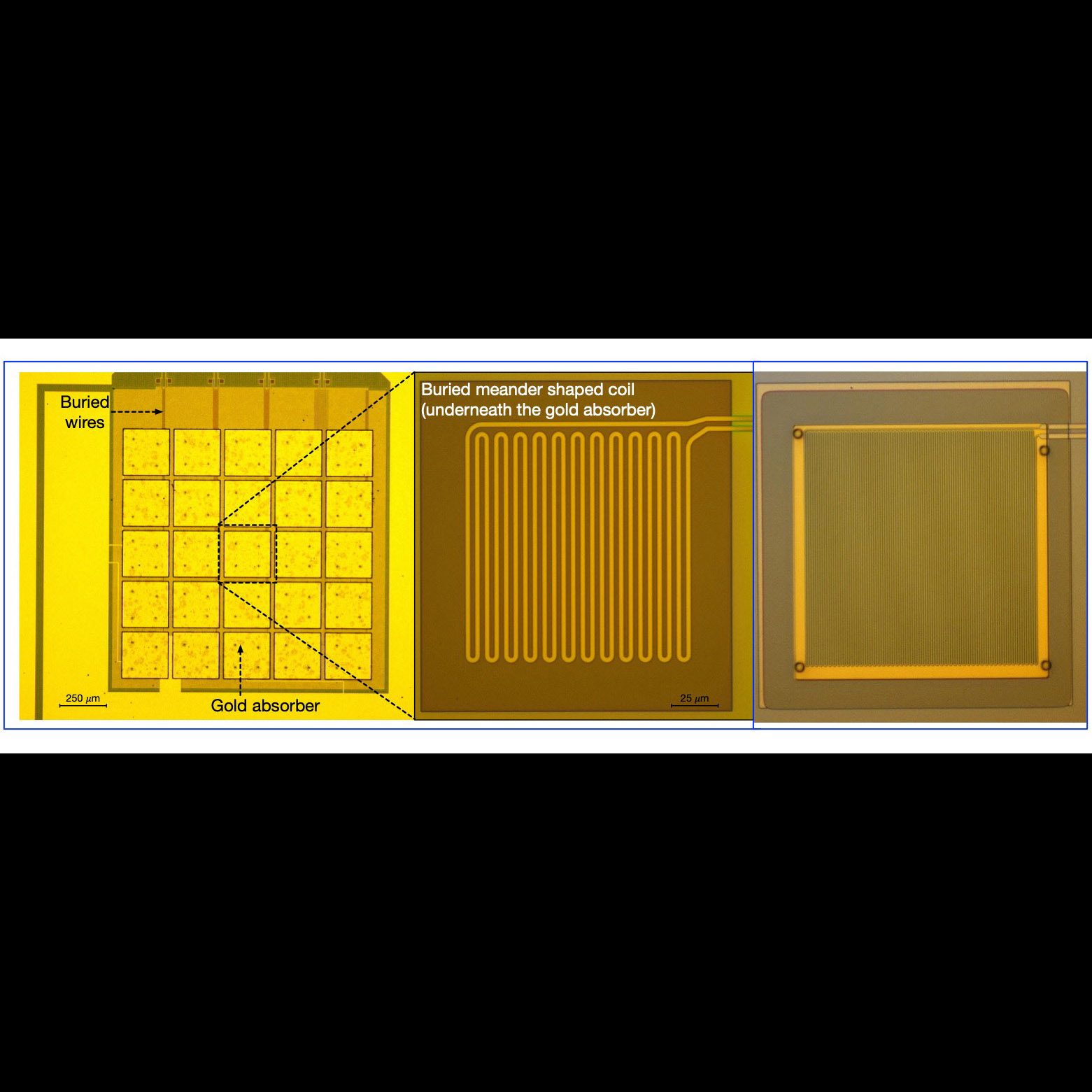
Significance: MMCs offer energy resolution that may enable future X-ray missions such as the Lynx X-ray flagship mission concept
Project Title: MMC Arrays for X-ray Astrophysics
PI: Simon Bandler (GSFC)

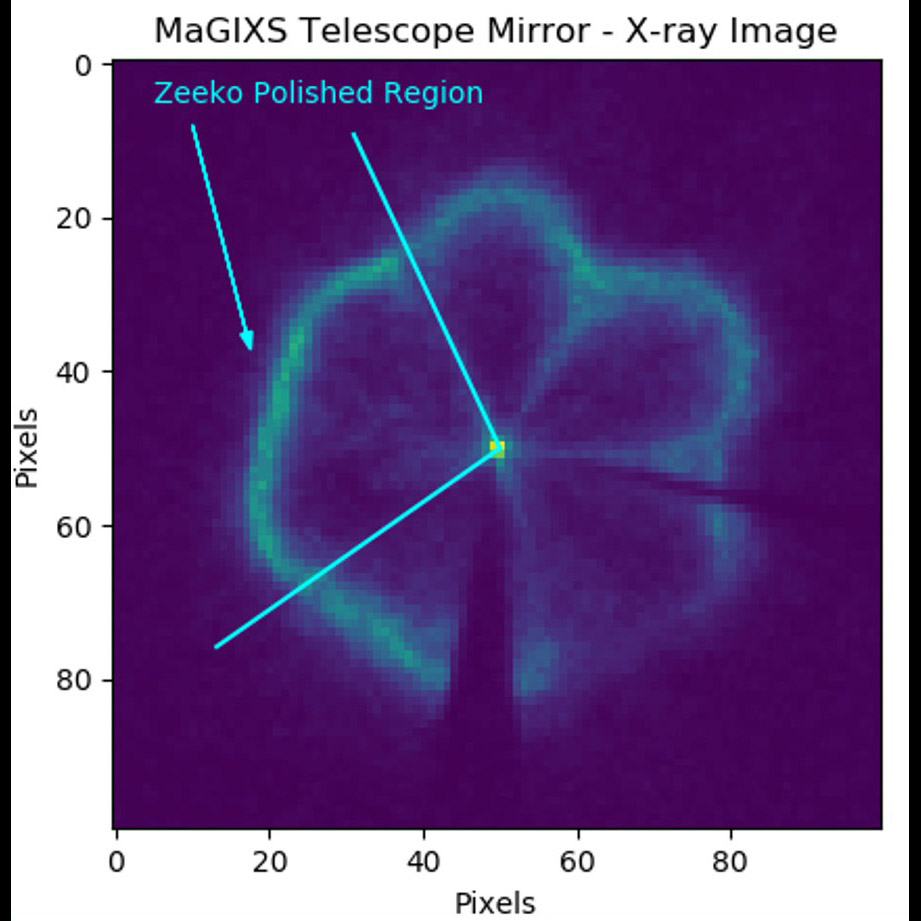
Significance: High-quality X-ray optics may enable or enhance future Astrophysics missions
Project Title: Advanced X-ray Optics: Computer-Controlled Polishing of High-Quality Mandrels
PI: Jacqueline Davis (MSFC)

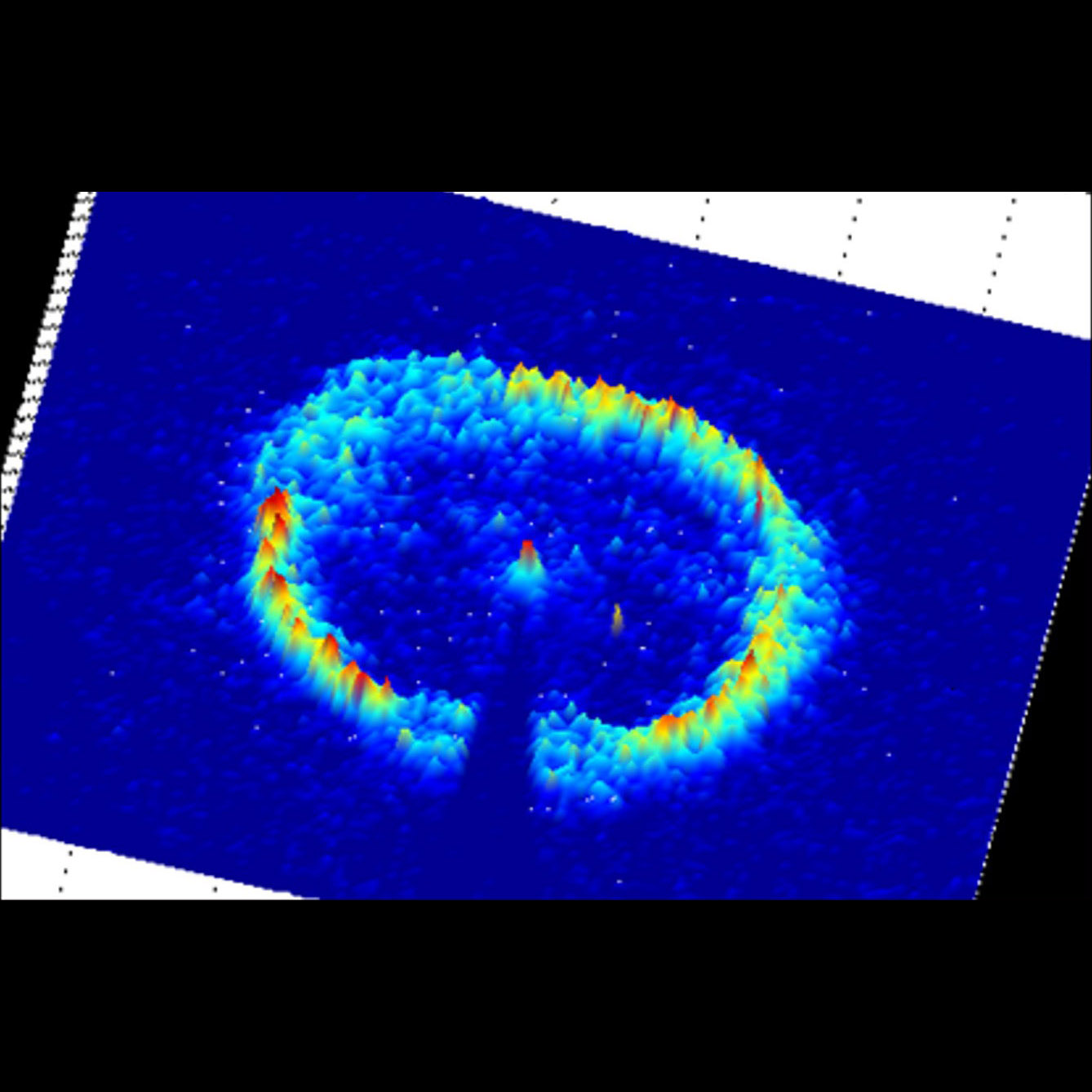
Significance: High-quality X-ray optics may enable or enhance future Astrophysics missions
Project Title: Advanced X-ray Optics: Differential Deposition for Figure Correction in X-Ray Optics
PI: Kiranmayee Kilaru (MSFC)
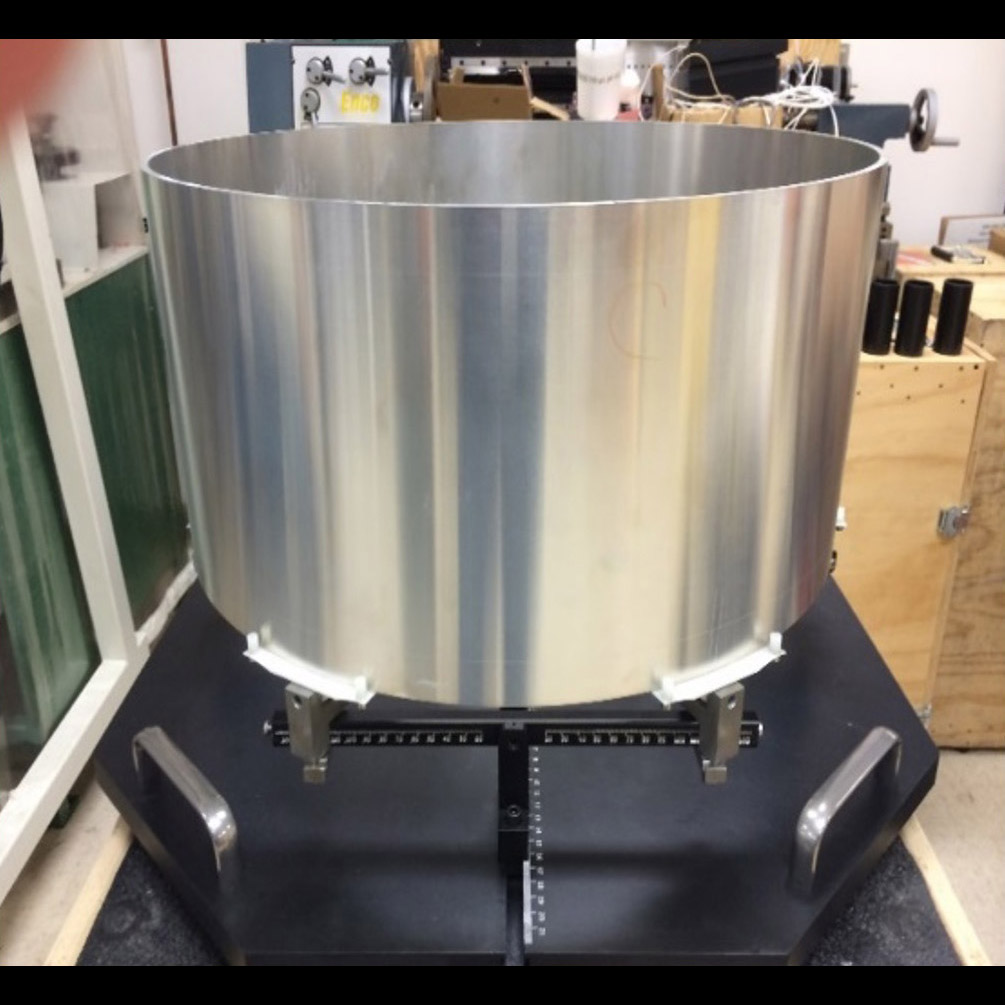


Significance: High-quality X-ray optics may enable future X-ray missions
Project Title: Advanced X-ray Optics: Full-Shell Direct Polishing
PI: Stephen Bongiorno (MSFC)


Significance: High-quality X-ray optics may enable future missions
Project Title: Advanced X-ray Optics: Mirror Coatings
PI: David Broadway (MSFC)
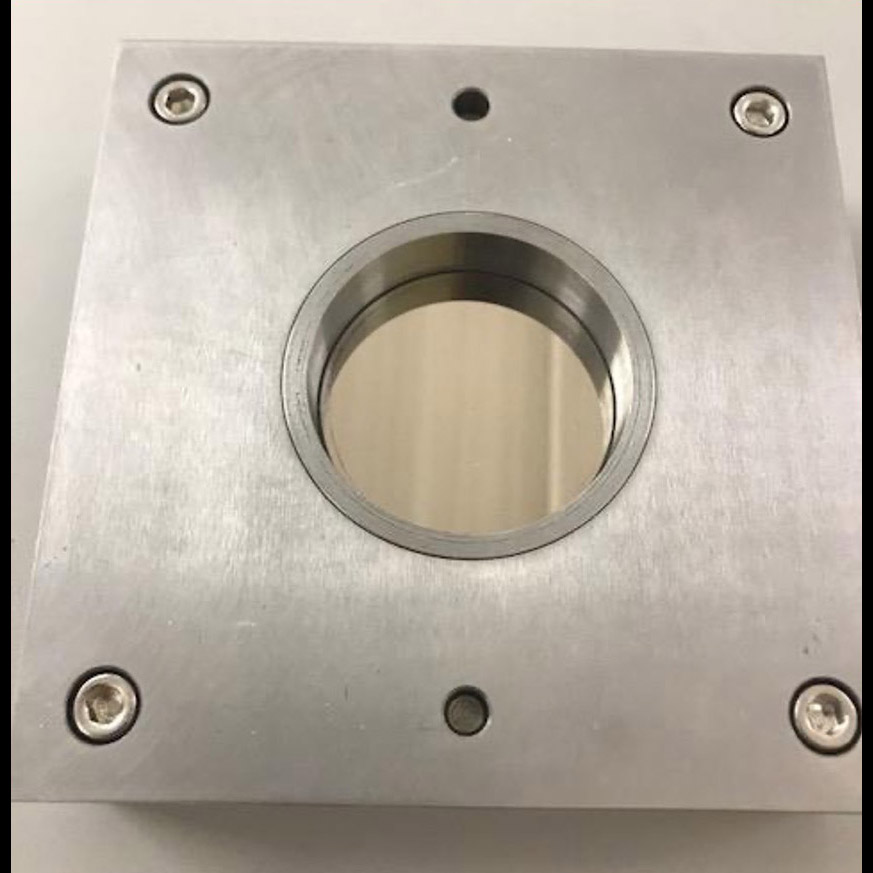


Significance: Low-cost, lightweight, high-quality X-ray optics may enable many future missions
Project Title: Advanced X-ray Optics: Hybrid X-Ray Optics by Additive Manufacturing
PI: David Broadway (MSFC)

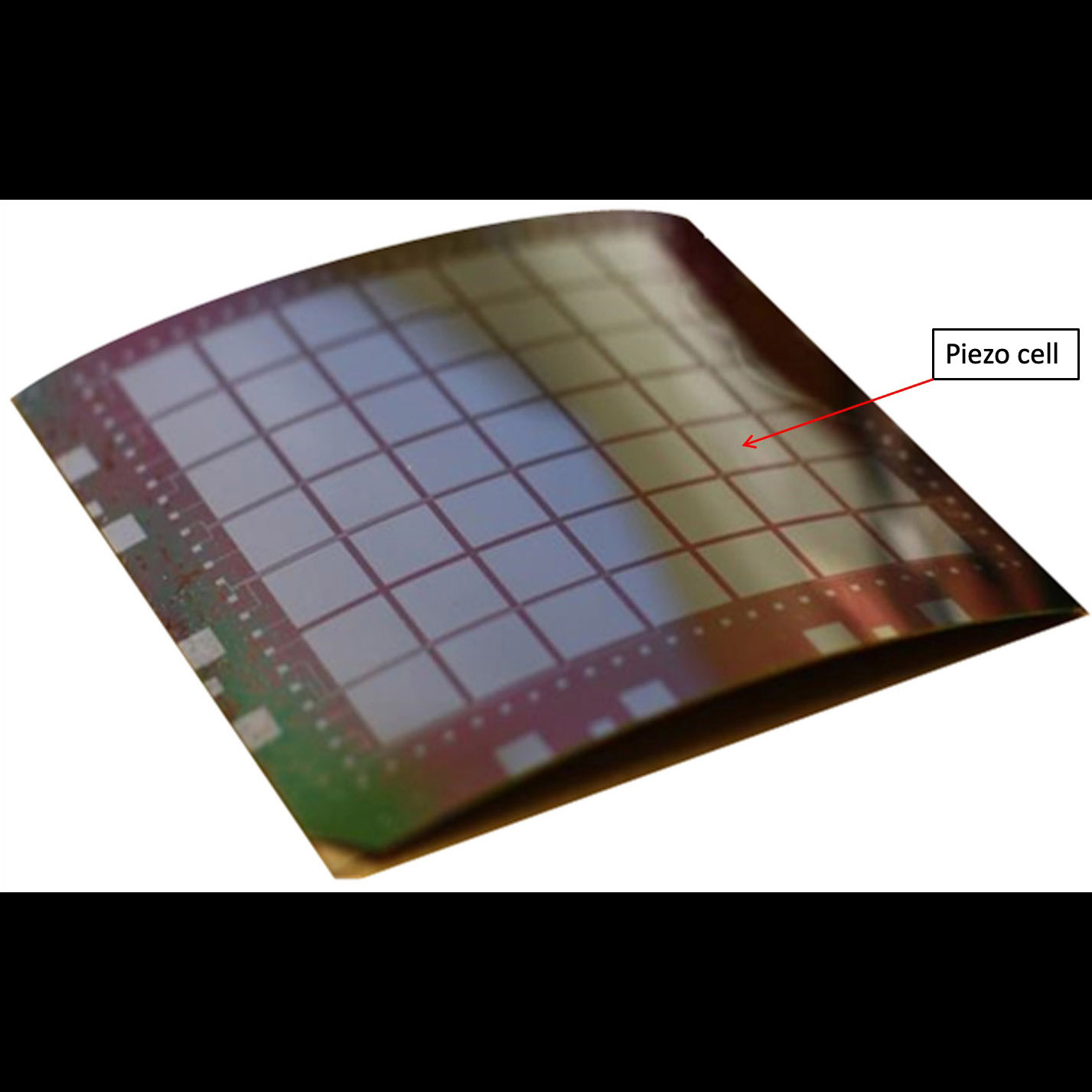
Significance: Adjustable X-ray optics are a backup technology for the Lynx X-ray large mission concept
Project Title: Adjustable X-Ray Optics
PI: Paul Reid (SAO)

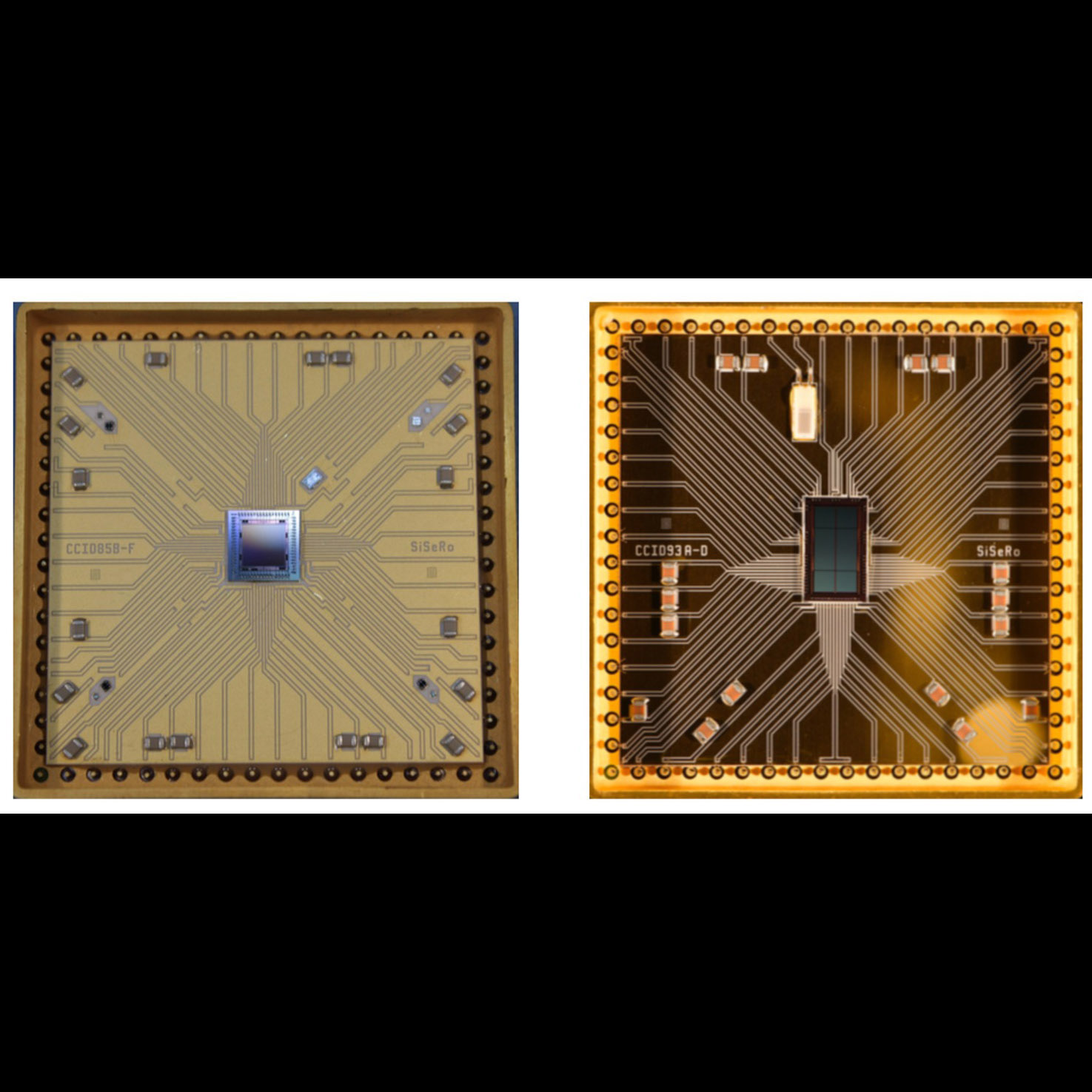
Significance: Advanced X-ray detectors may enable the Lynx large mission concept
Project Title: Toward Fast, Low-Noise, Radiation Tolerant X-ray Imaging Arrays for Lynx: Raising Technology Readiness Further
PI: Mark Bautz (MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research)

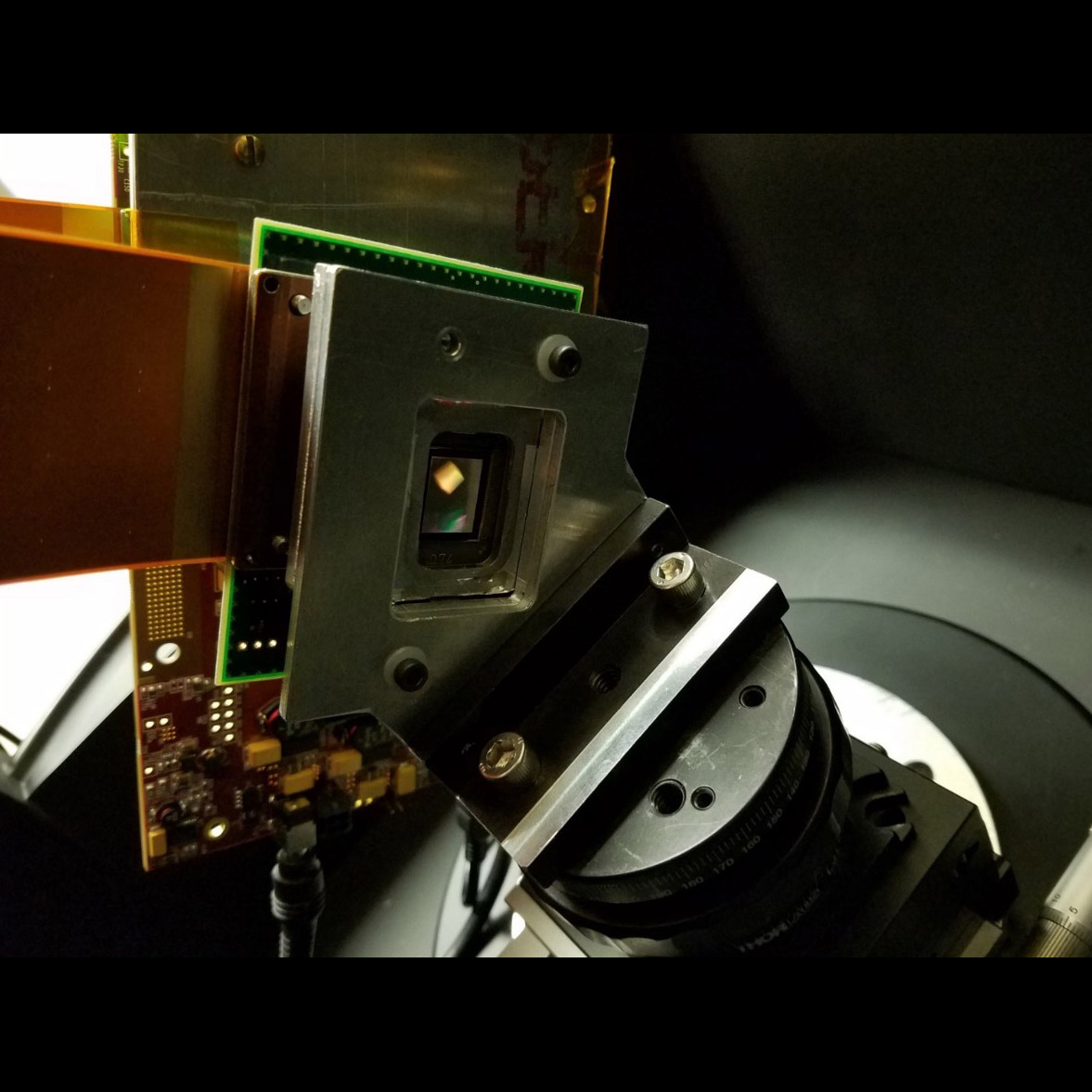
Significance: Replacing windows of commercially available DMDs may enable far-UV multi-object spectrometry in future missions
Project Title: Development of DMDs for Far-UV Applications
PI: Zoran Ninkov (RIT)

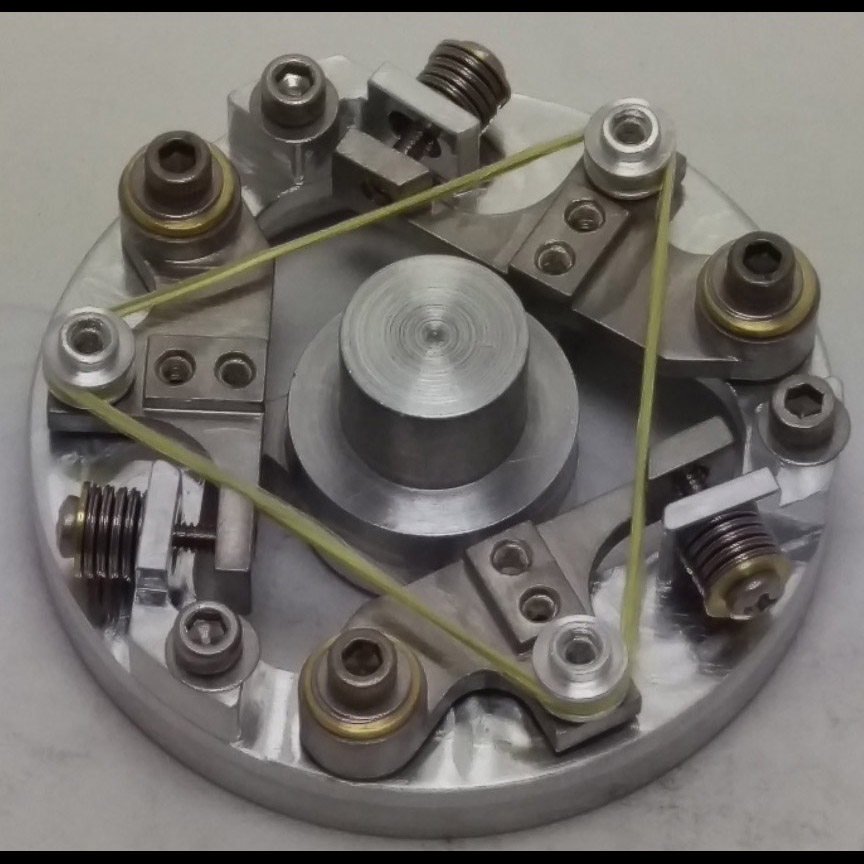
Significance: This advanced sub-Kelvin cooling technology has been baselined by Lynx, Origins, PICO, and GEP
Project Title: High-Efficiency Continuous Cooling for Cryogenic Instruments and sub-Kelvin Detectors
PI: James Tuttle (GSFC)

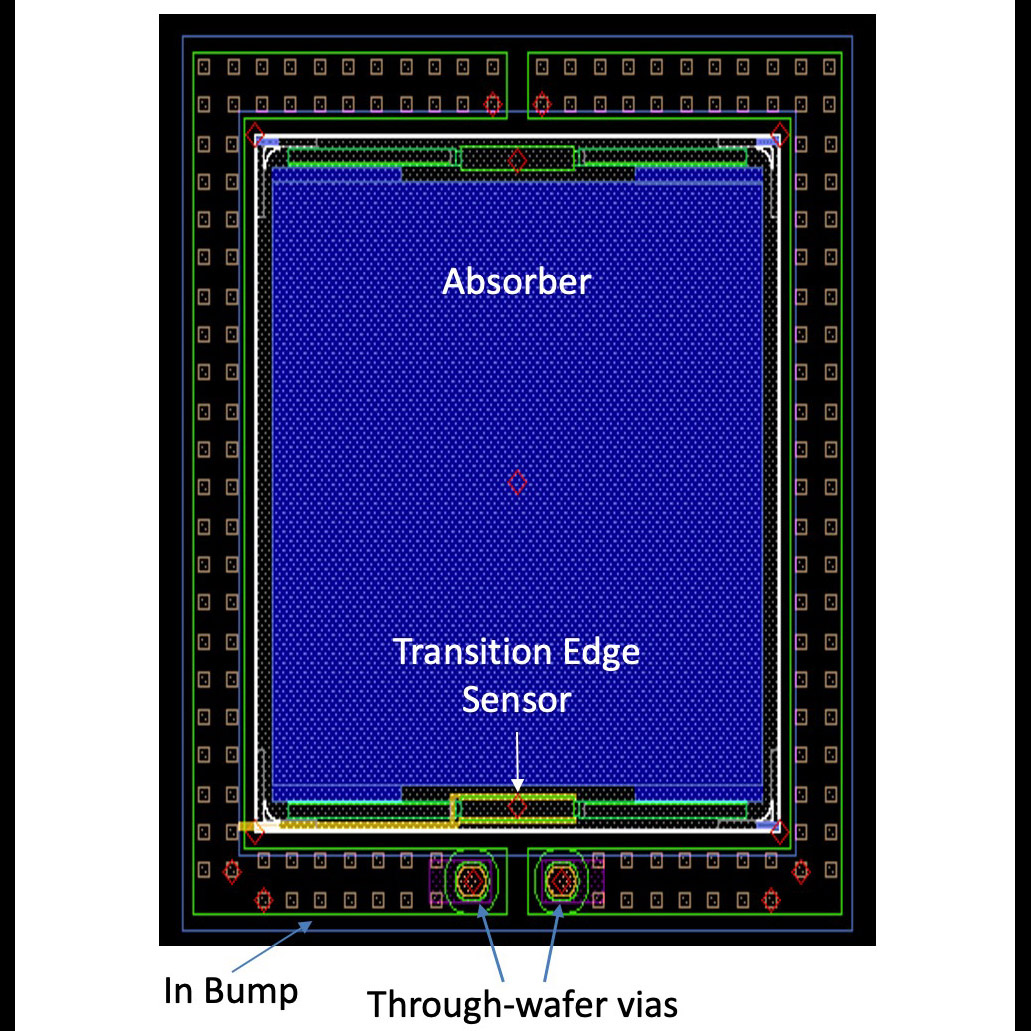
Significance: This new technique may enable the Origins large mission concept
Project Title: Development of a Robust, Efficient Process to Produce Scalable, Superconducting Kilopixel Far-IR Detector Arrays
PI: Johannes Staguhn (JHU & GSFC)
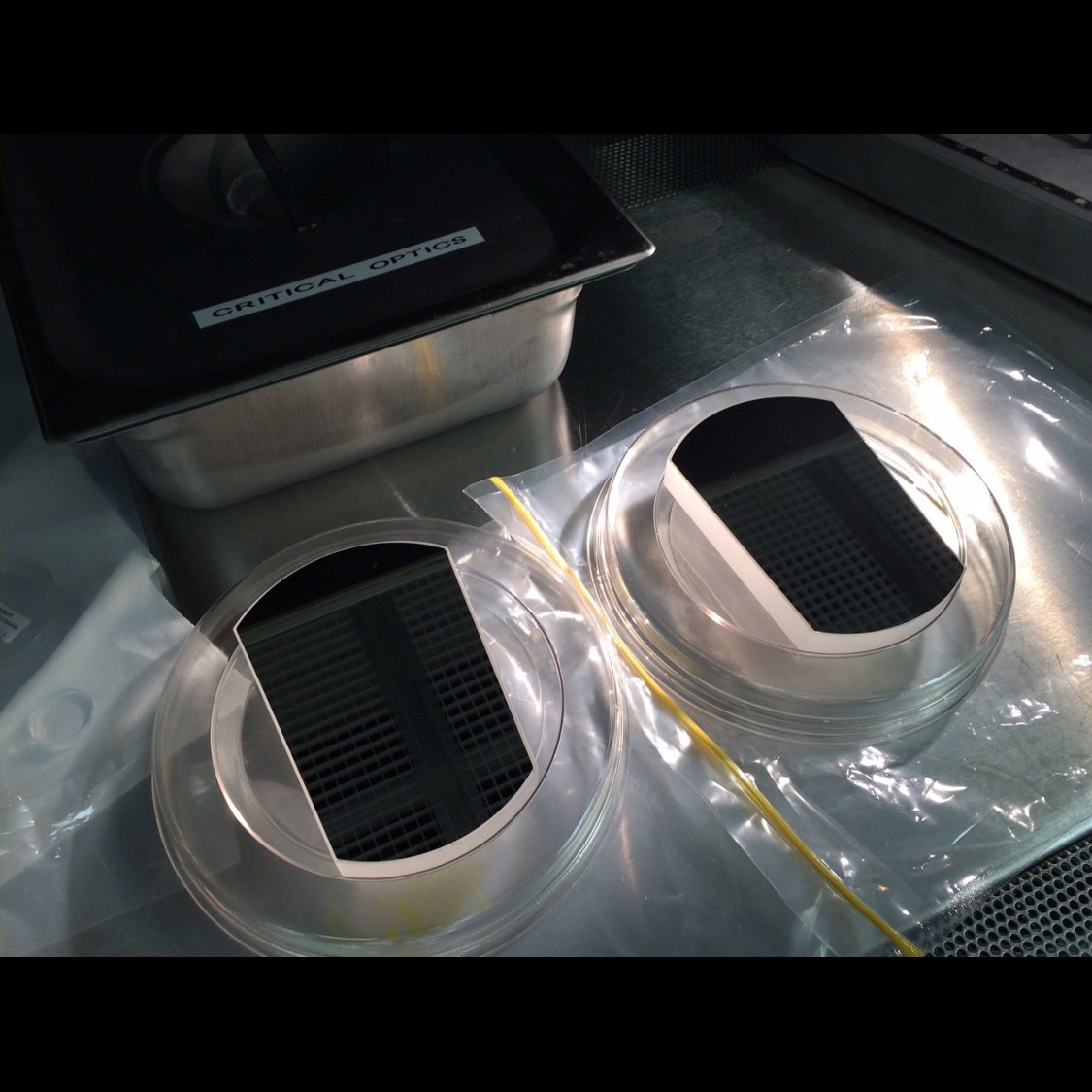


Significance: High far-UV reflectance is prevented by oxidation of aluminum mirrors; removing it may enable future far-UV missions
Project Title: E-Beam-Generated Plasma Etching for Developing High-Reflectance Mirrors for Far-UV Astronomical Instrument Applications
PI: Manuel Quijada (GSFC)

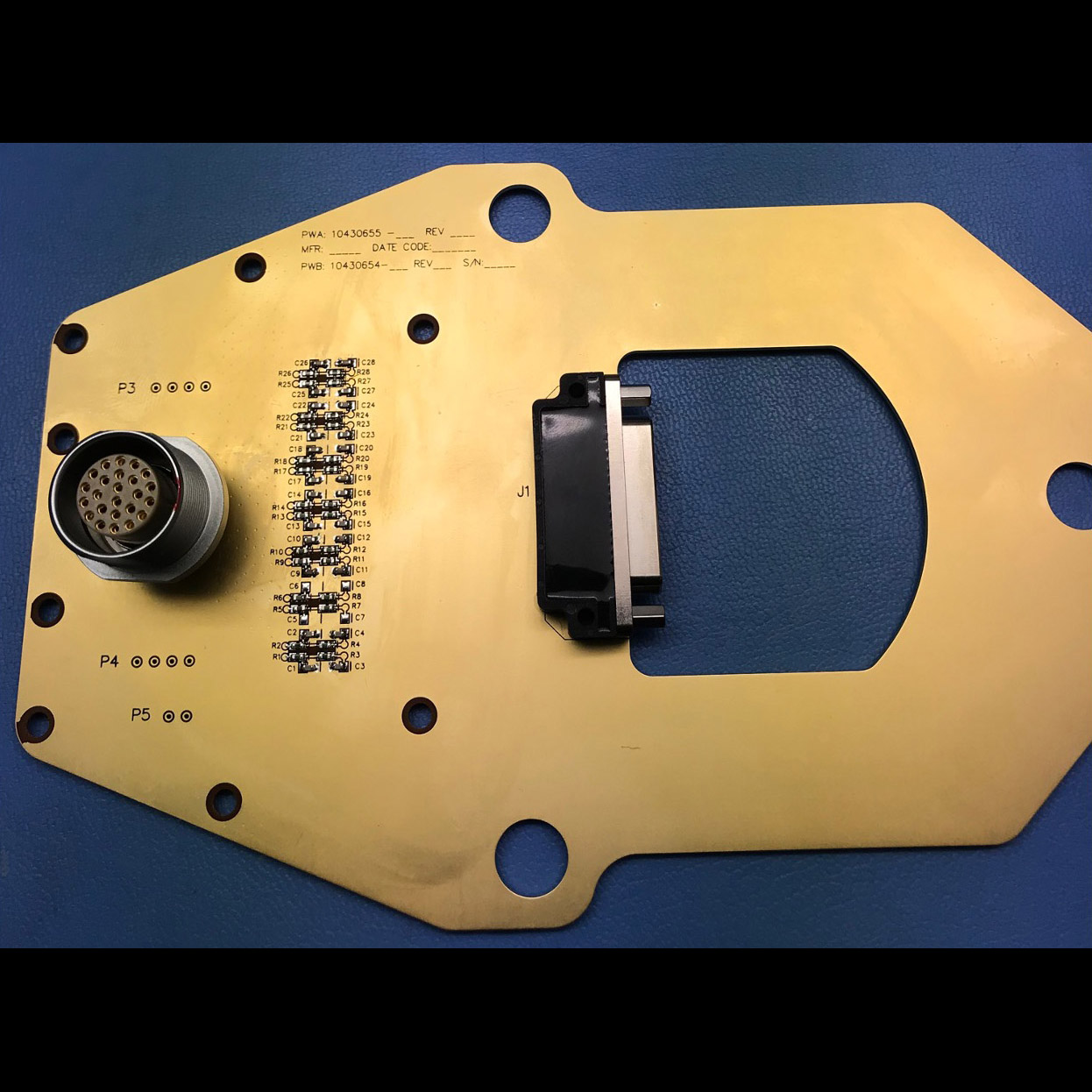
Significance: Extremely sensitive far-IR detectors may enable future missions
Project Title: Ultra-Sensitive Bolometers for Far-IR Space Spectroscopy at the Background Limit
PI: C. Matt Bradford (JPL)


Significance: Further development of this high-resolution far-IR detector technology to higher pixel numbers may enable or enhance future missions
Project Title: Development of High-Resolution Far-IR Arrays
PI: Imran Mehdi (JPL)

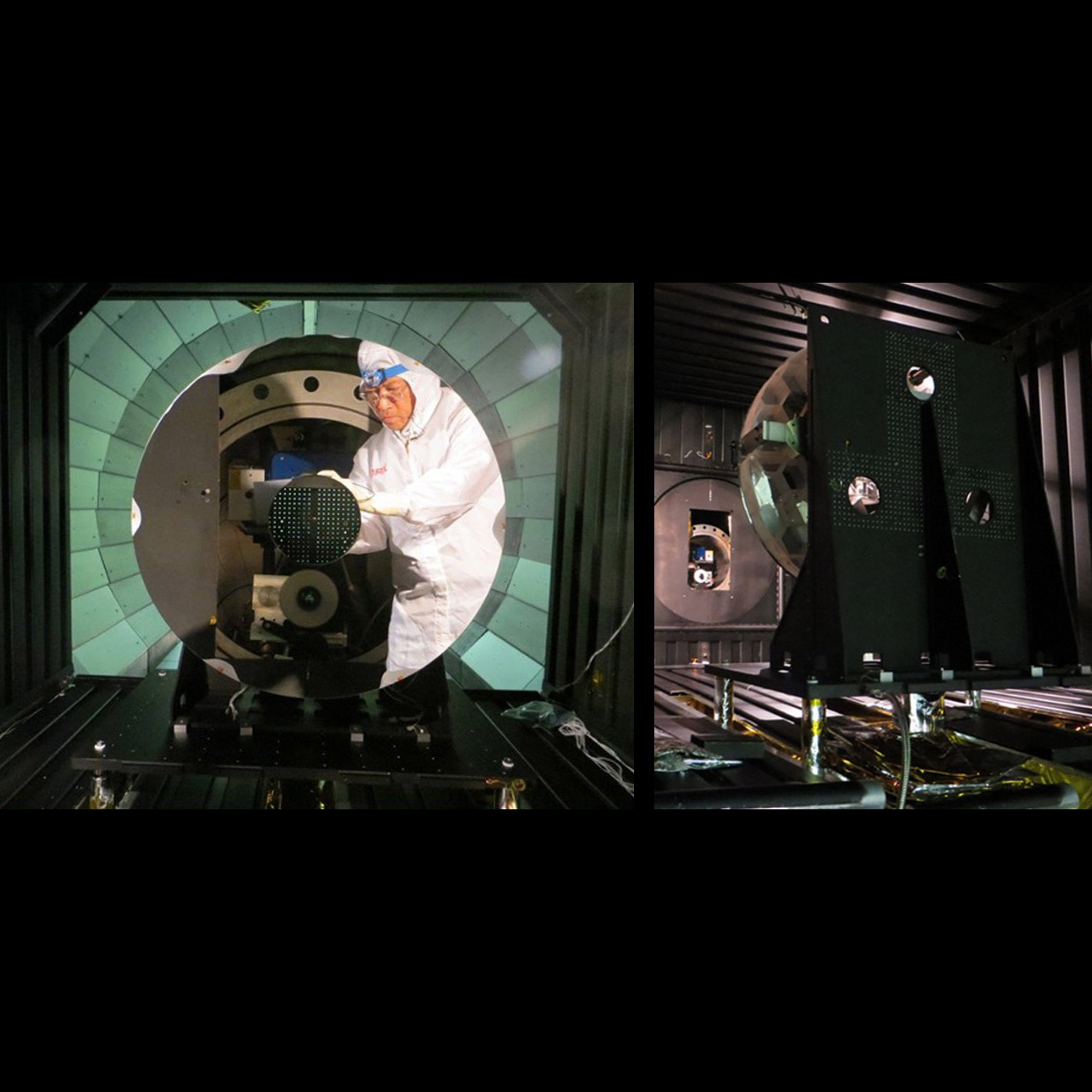
Significance: This technology may enable required ultra-stability (~10 pm) for HabEx and LUVOIR missions
Project Title: Predictive Thermal Control (PTC) Technology to enable Thermally Stable Telescopes
PI: H. Philip Stahl (MSFC)

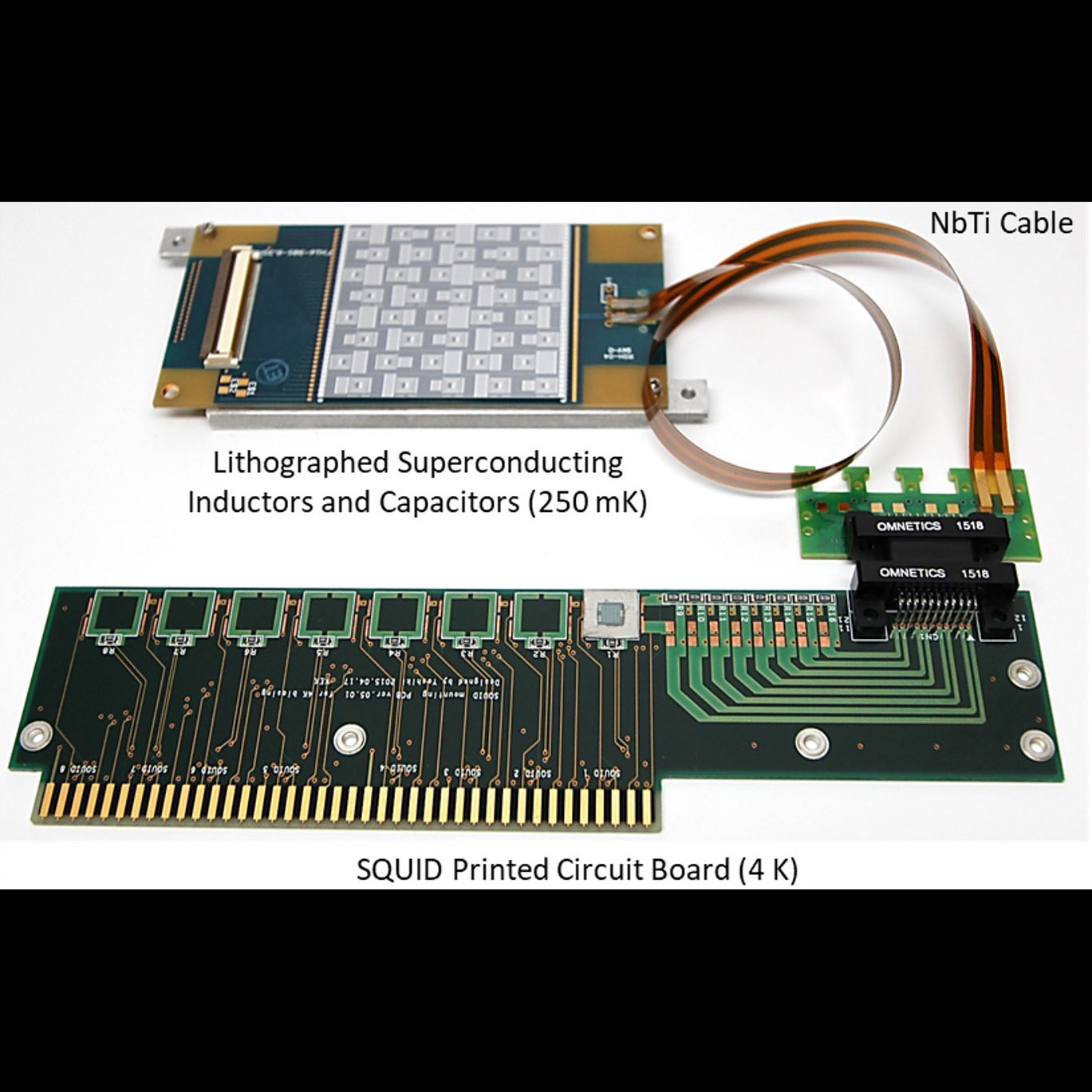
Significance: This and related technologies may enable future Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) missions, e.g. LiteBIRD
Project Title: Technology Development for LiteBIRD and other CMB Missions
PI: Adrian T. Lee (UC Berkeley)

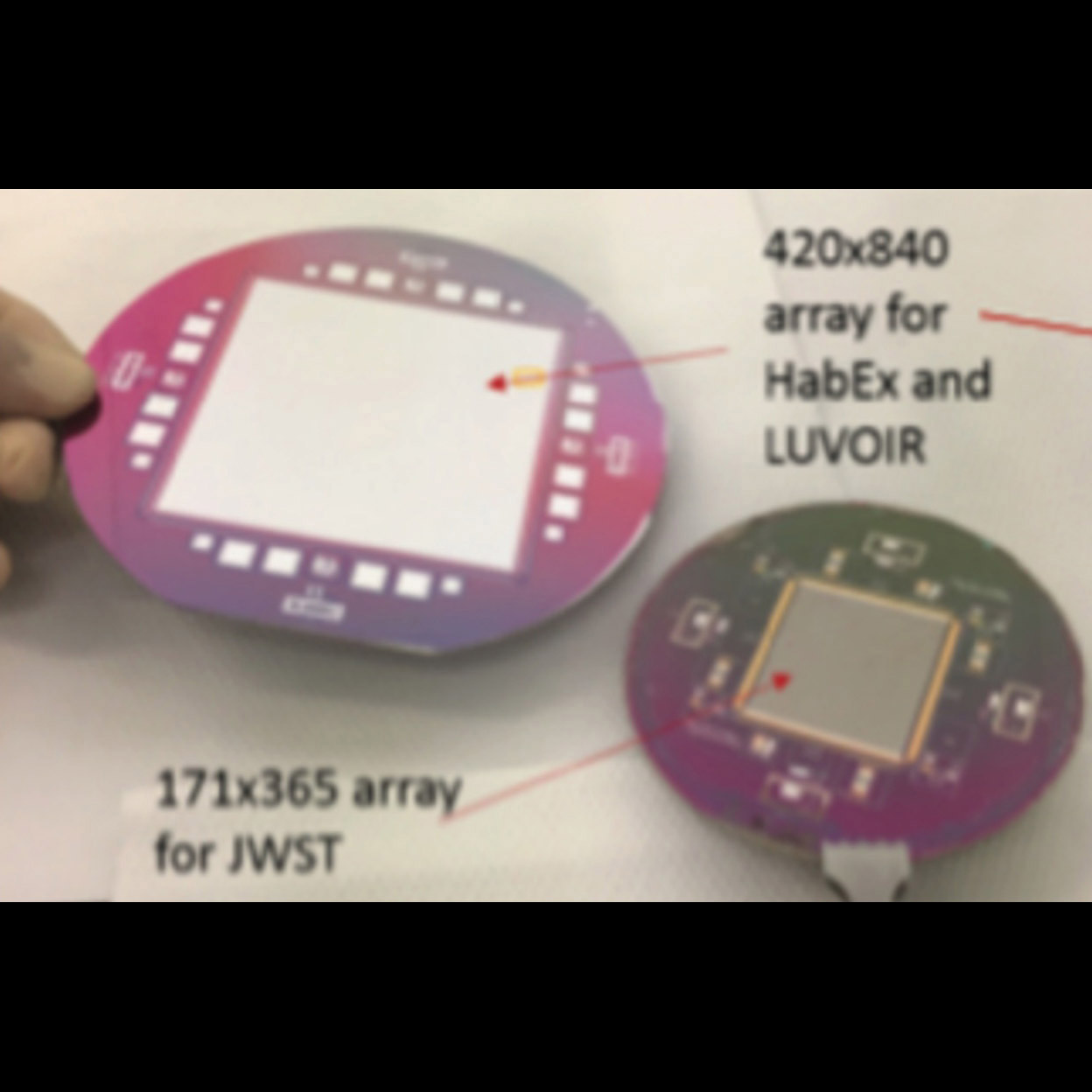
Significance:May enable sparse-field multi-object spectroscopy for e.g. LUVOIR, HabEx, CETUS, and/or AERIE
Project Title: Scalable Microshutter Systems for UV, Visible, and IR Spectroscopy
PI: Matt Greenhouse (GSFC)

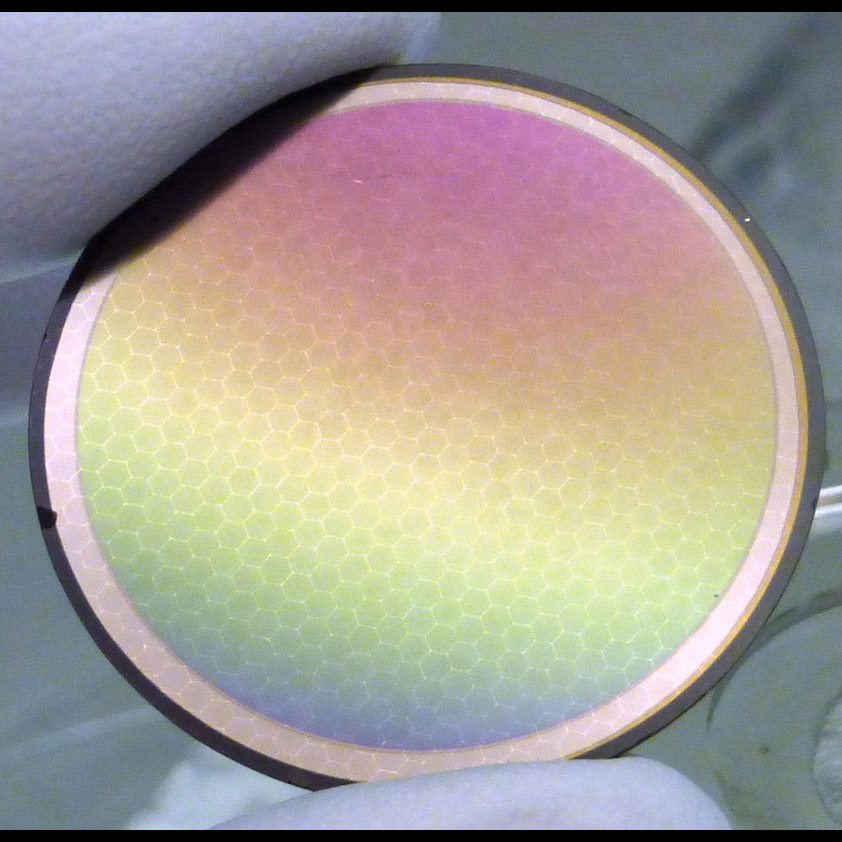
Significance: This detector technology is baselined by HabEx, LUVOIR, and CETUS for UV/Visible light detection
Project Title: High-Performance Sealed-Tube Cross-Strip (XS) Photon-Counting Sensors for UV-Vis Astrophysics Instruments
PI: Oswald Siegmund (UC Berkeley)

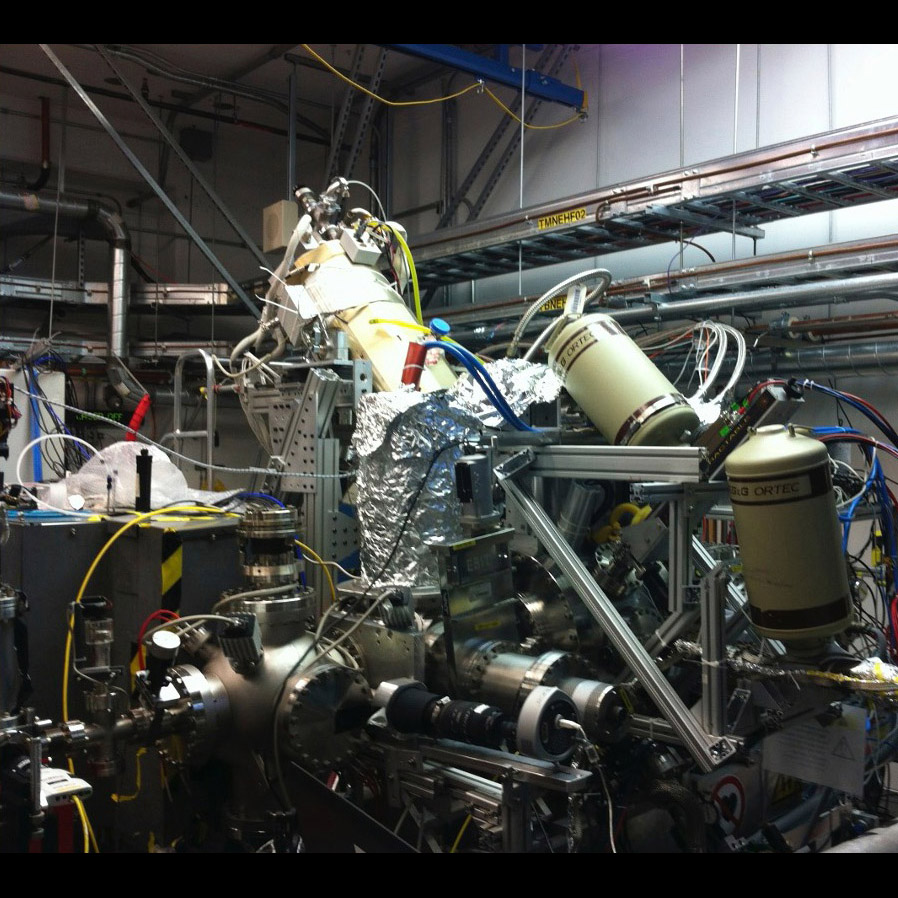
Significance: The project supports NASA X-ray observatories by developing similar instruments in ground-based labs, replicating conditions in astrophysical sources observed by spaceflight instruments, and observing them parametrically to help interpret space-based data
Project Title: Advanced X-ray Microcalorimeters: Lab Spectroscopy for Space Atomic Physics
PI: F. Scott Porter (GSFC)

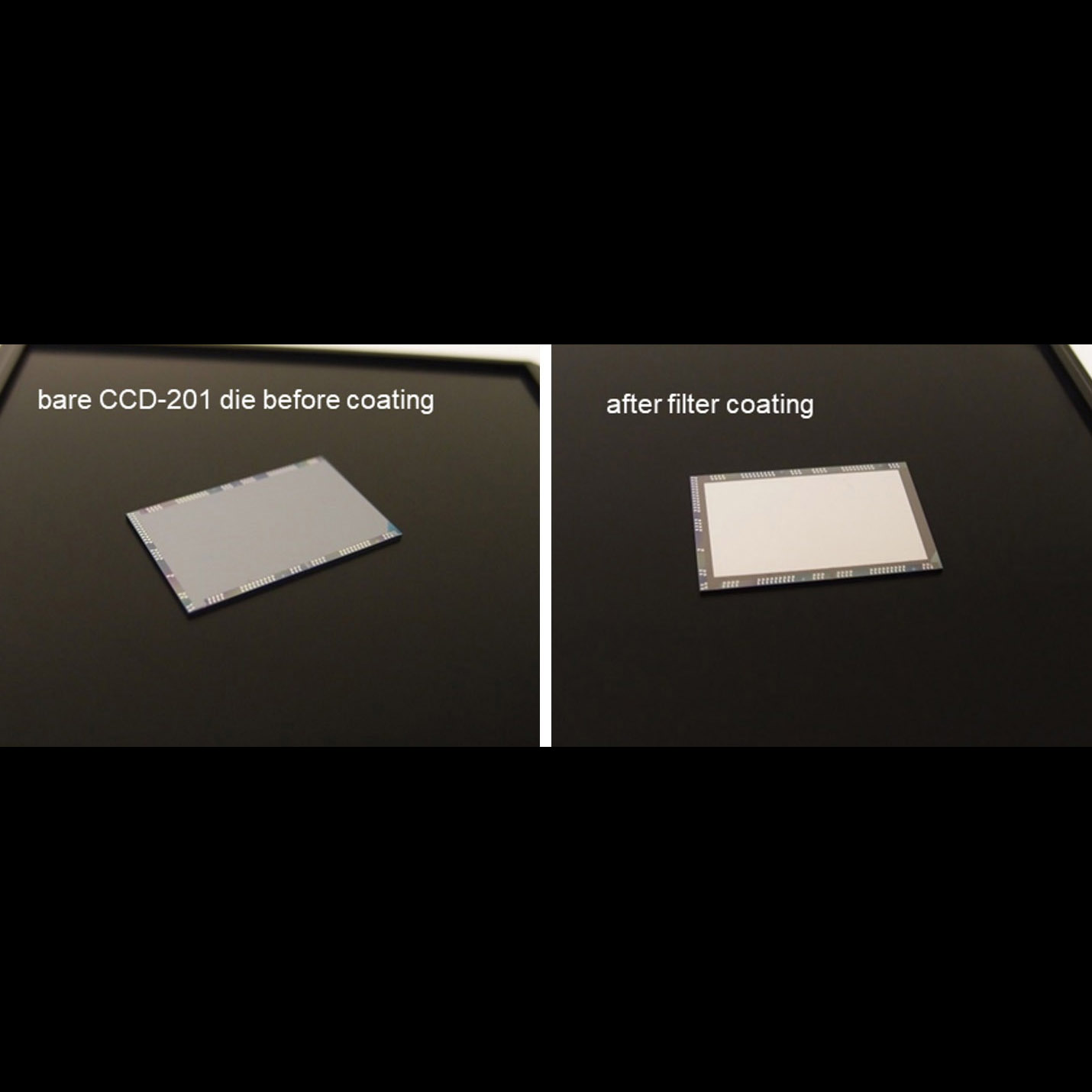
Significance: Advanced detectors developed by this project are baselined by SHIELDS, HabEx, LUVOIR, and ground facilities are fabricated using Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) coatin
Project Title: Advanced FUV/UV/Visible Photon-Counting and Ultralow-Noise Detectors
PI: Shouleh Nikzad (JPL/Caltech)

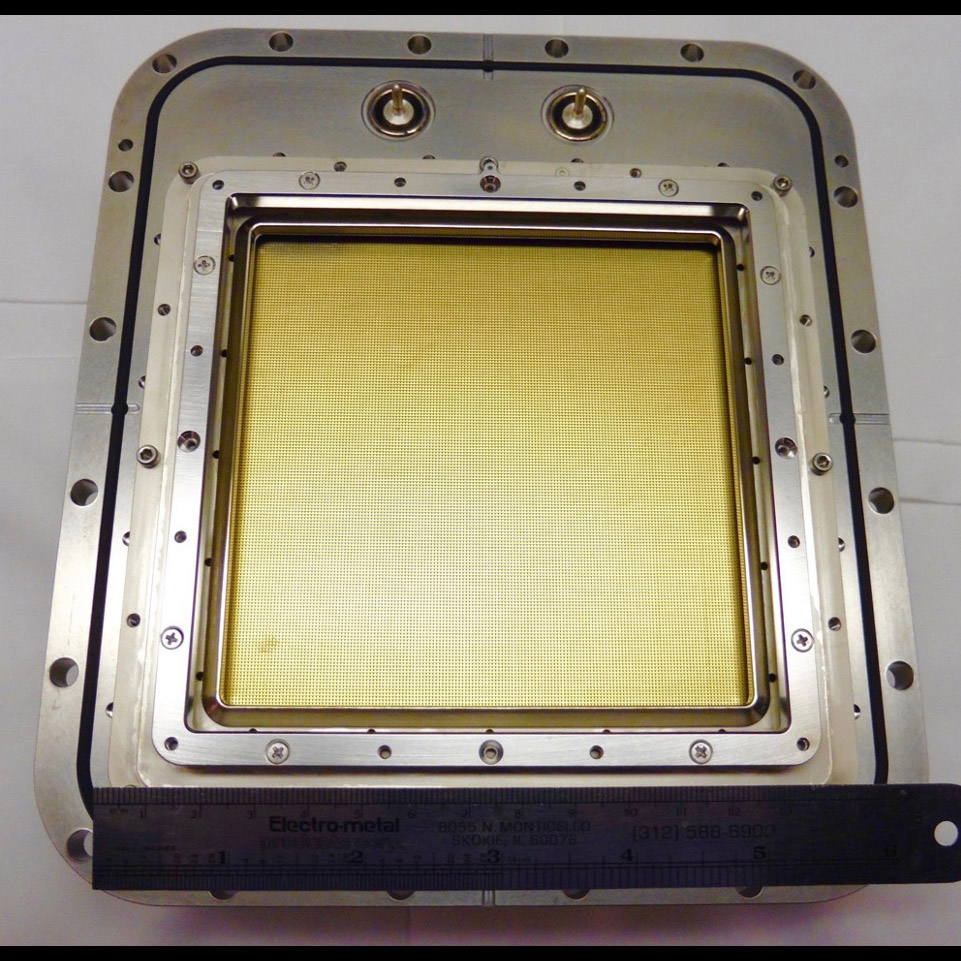
Significance: Large-format low-noise detectors may enable future far-UV missions
Project Title: Development of 100×100 mm2 photon-counting UV detectors
PI: John Vallerga (UC Berkeley)

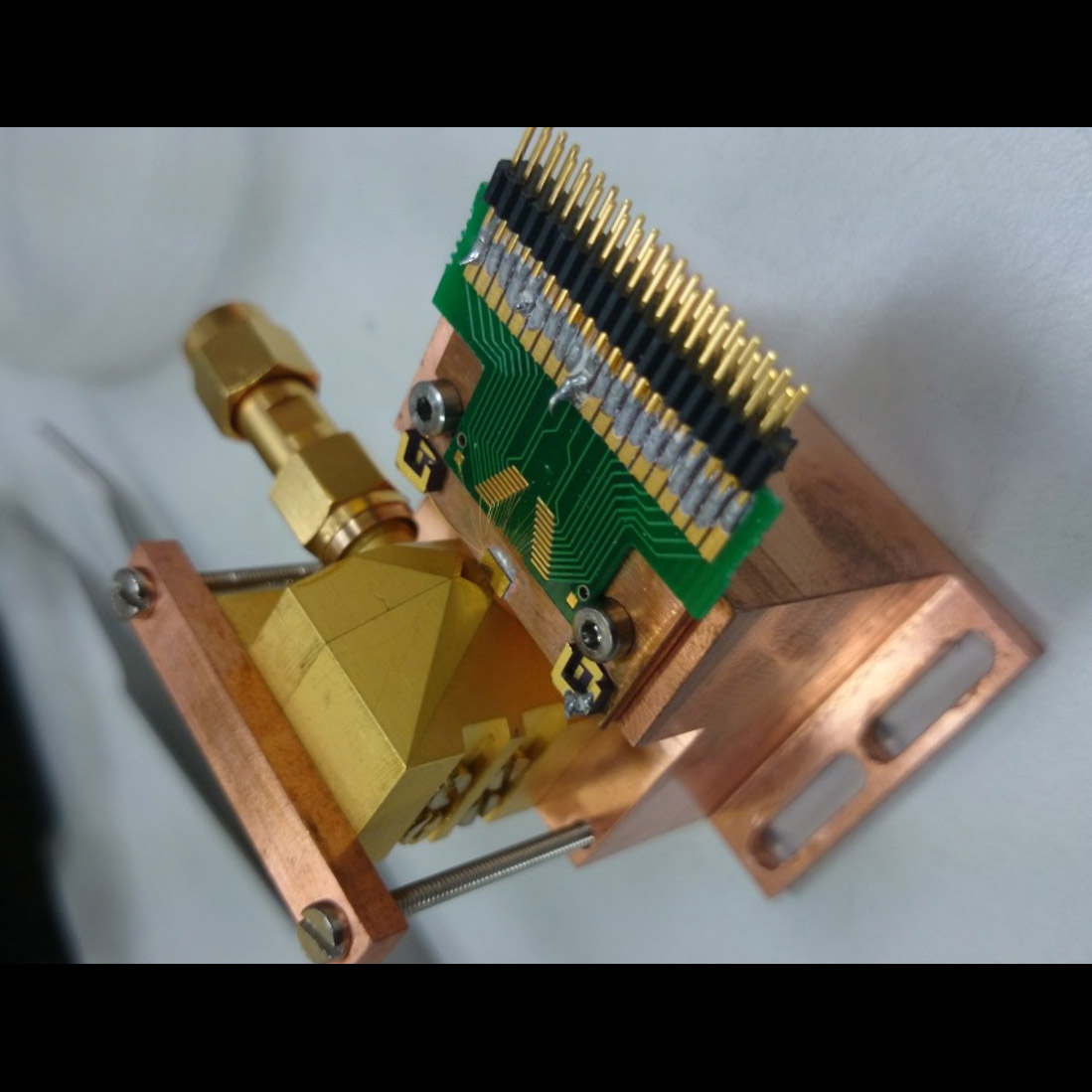
Significance: This technology provides 4.7-THz LOs, enabling far-IR/sub-mm missions such as the balloon-borne Galactic/Extragalactic ULDB Spectroscopic Terahertz Observatory (GUSTO)
Project Title: Raising the Technology Readiness of 4.7-THz local oscillators
PI: Qing Hu (MIT)
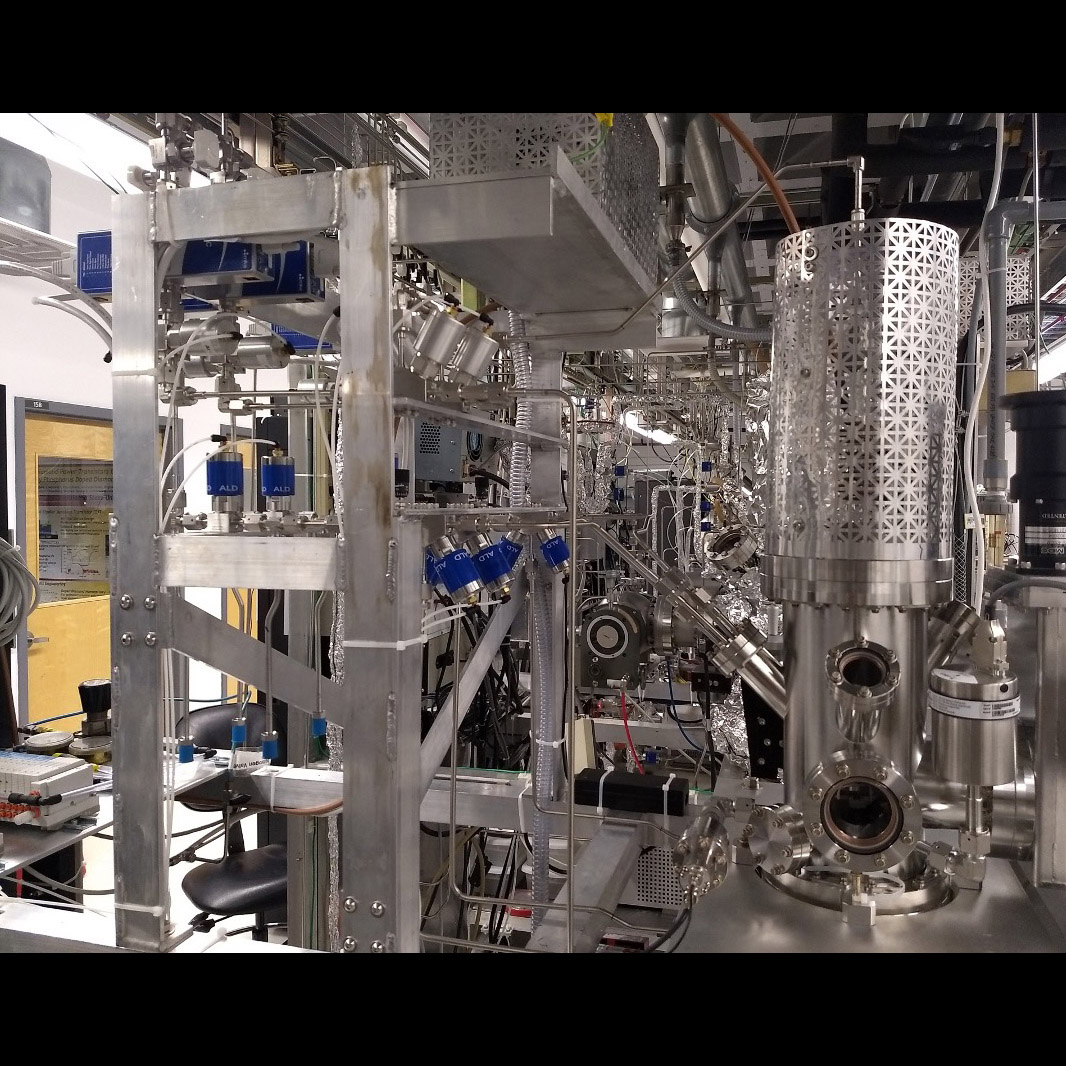


Significance: High-reflectance UV coatings would vastly improve system throughput for photon-starved UV astronomy; this system attempted to develop advanced technique for depositing high-reflectance UV coatings
Project Title: Improving UV Coatings and Filters using Innovative Materials Deposited by ALD
PI: Paul Scowen (ASU)
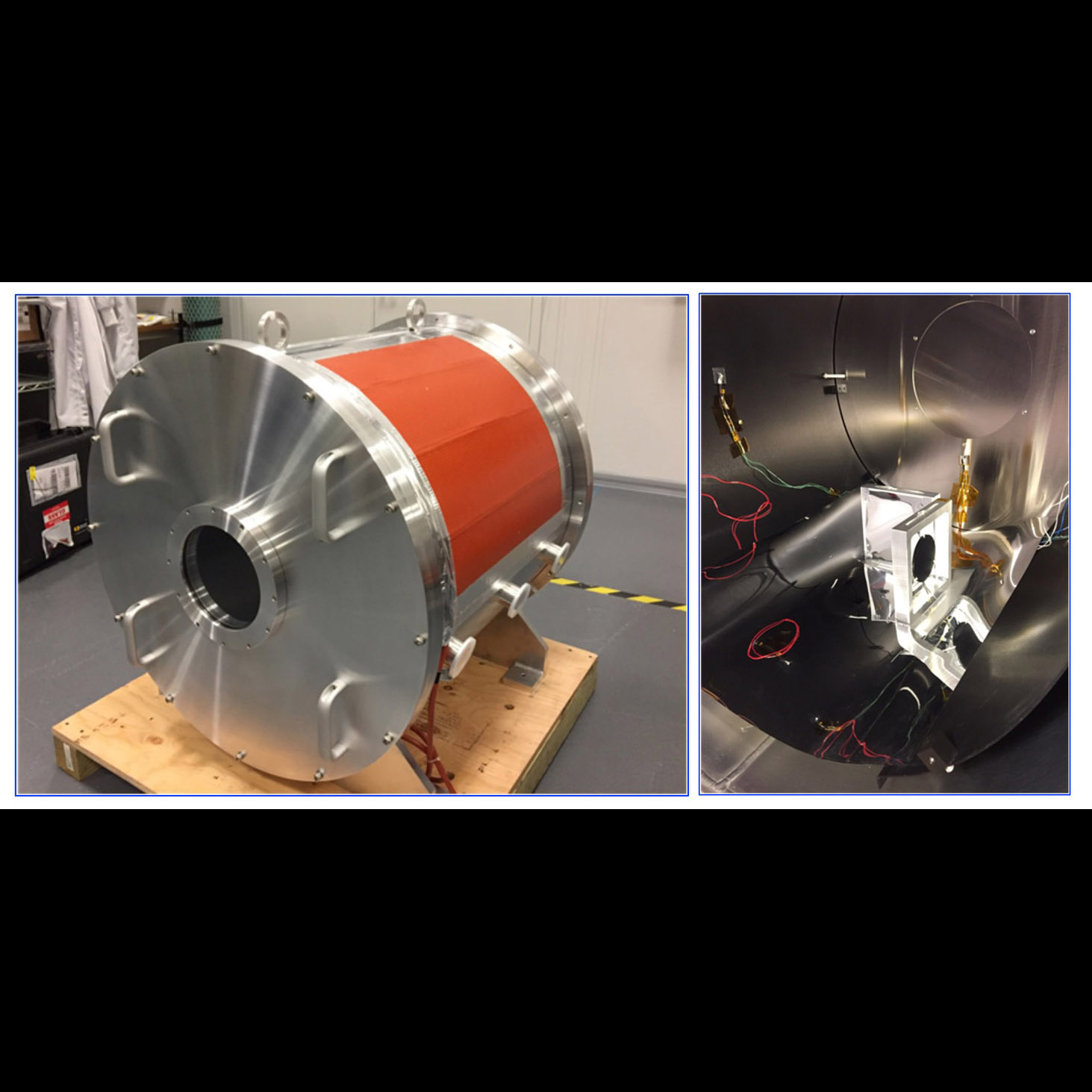


Significance: Ultra-stability and -precision (~10 pm) may enable the HabEx and LUVOIR missions
Project Title: Ultra-Stable Structures
PI: Babak Saif (GSFC)


For more information about these technologies visit our Technology Database.

Significance: World-class thin grazing-angle X-ray mirror technology; baselined for Lynx X-ray flagship mission concept
Project Title: Next Generation X-ray Optics: High Resolution, Light Weight, and Low Cost
PI: Zhang, William (GSFC)

Significance: Highest-resolution X-ray grating technology; baselined for Lynx X-ray flagship mission concept
Project Title: Development of a CAT Grating Spectromete
PI: Mark Schattenburg (MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research)

Significance: Developing antenna designs providing sensitivity, stability, and minimized particle susceptibility for bands required by the Inflation Probe, enabling identification of Inflation instants after the Big Bang
Project Title: Planar Antenna-Coupled Superconducting Detectors for CMB Polarimetry
PI: James Bock (JPL/Caltech)

Significance: TES microcalorimeters offer energy resolution that may enable future missions such as the Lynx X-ray flagship mission concept
Project Title: Advanced X-ray Microcalorimeters: TES Microcalorimeters
PI: Caroline Kilbourne (GSFC)

Significance: MMCs offer energy resolution that may enable future X-ray missions such as the Lynx X-ray flagship mission concept
Project Title: MMC Arrays for X-ray Astrophysics
PI: Simon Bandler (GSFC)

Significance: High-quality X-ray optics may enable or enhance future Astrophysics missions
Project Title: Advanced X-ray Optics: Computer-Controlled Polishing of High-Quality Mandrels
PI: Jacqueline Davis (MSFC)

Significance: High-quality X-ray optics may enable or enhance future Astrophysics missions
Project Title: Advanced X-ray Optics: Differential Deposition for Figure Correction in X-Ray Optics
PI: Kiranmayee Kilaru (MSFC)

Significance: High-quality X-ray optics may enable future X-ray missions
Project Title: Advanced X-ray Optics: Full-Shell Direct Polishing
PI: Stephen Bongiorno (MSFC)

Significance: High-quality X-ray optics may enable future missions
Project Title: Advanced X-ray Optics: Mirror Coatings
PI: David Broadway (MSFC)

Significance: Low-cost, lightweight, high-quality X-ray optics may enable many future missions
Project Title: Advanced X-ray Optics: Hybrid X-Ray Optics by Additive Manufacturing
PI: David Broadway (MSFC)

Significance: Adjustable X-ray optics are a backup technology for the Lynx X-ray large mission concept
Project Title: Adjustable X-Ray Optics
PI: Paul Reid (SAO)

Significance: Advanced X-ray detectors may enable the Lynx large mission concept
Project Title: Toward Fast, Low-Noise, Radiation Tolerant X-ray Imaging Arrays for Lynx: Raising Technology Readiness Further
PI: Mark Bautz (MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research)

Significance: Replacing windows of commercially available DMDs may enable far-UV multi-object spectrometry in future missions
Project Title: Development of DMDs for Far-UV Applications
PI: Zoran Ninkov (RIT)

Significance: This advanced sub-Kelvin cooling technology has been baselined by Lynx, Origins, PICO, and GEP
Project Title: High-Efficiency Continuous Cooling for Cryogenic Instruments and sub-Kelvin Detectors
PI: James Tuttle (GSFC)

Significance: This new technique may enable the Origins large mission concept
Project Title: Development of a Robust, Efficient Process to Produce Scalable, Superconducting Kilopixel Far-IR Detector Arrays
PI: Johannes Staguhn (JHU & GSFC)

Significance: High far-UV reflectance is prevented by oxidation of aluminum mirrors; removing it may enable future far-UV missions
Project Title: E-Beam-Generated Plasma Etching for Developing High-Reflectance Mirrors for Far-UV Astronomical Instrument Applications
PI: Manuel Quijada (GSFC)

Significance: Extremely sensitive far-IR detectors may enable future missions
Project Title: Ultra-Sensitive Bolometers for Far-IR Space Spectroscopy at the Background Limit
PI: C. Matt Bradford (JPL)

Significance: Further development of this high-resolution far-IR detector technology to higher pixel numbers may enable or enhance future missions
Project Title: Development of High-Resolution Far-IR Arrays
PI: Imran Mehdi (JPL)

Significance: This technology may enable required ultra-stability (~10 pm) for HabEx and LUVOIR missions
Project Title: Predictive Thermal Control (PTC) Technology to enable Thermally Stable Telescopes
PI: H. Philip Stahl (MSFC)

Significance: This and related technologies may enable future Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) missions, e.g. LiteBIRD
Project Title: Technology Development for LiteBIRD and other CMB Missions
PI: Adrian T. Lee (UC Berkeley)

Significance:May enable sparse-field multi-object spectroscopy for e.g. LUVOIR, HabEx, CETUS, and/or AERIE
Project Title: Scalable Microshutter Systems for UV, Visible, and IR Spectroscopy
PI: Matt Greenhouse (GSFC)

Significance: This detector technology is baselined by HabEx, LUVOIR, and CETUS for UV/Visible light detection
Project Title: High-Performance Sealed-Tube Cross-Strip (XS) Photon-Counting Sensors for UV-Vis Astrophysics Instruments
PI: Oswald Siegmund (UC Berkeley)

Significance: The project supports NASA X-ray observatories by developing similar instruments in ground-based labs, replicating conditions in astrophysical sources observed by spaceflight instruments, and observing them parametrically to help interpret space-based data
Project Title: Advanced X-ray Microcalorimeters: Lab Spectroscopy for Space Atomic Physics
PI: F. Scott Porter (GSFC)

Significance: Advanced detectors developed by this project are baselined by SHIELDS, HabEx, LUVOIR, and ground facilities are fabricated using Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) coatin
Project Title: Advanced FUV/UV/Visible Photon-Counting and Ultralow-Noise Detectors
PI: Shouleh Nikzad (JPL/Caltech)

Significance: Large-format low-noise detectors may enable future far-UV missions
Project Title: Development of 100×100 mm2 photon-counting UV detectors
PI: John Vallerga (UC Berkeley)

Significance: This technology provides 4.7-THz LOs, enabling far-IR/sub-mm missions such as the balloon-borne Galactic/Extragalactic ULDB Spectroscopic Terahertz Observatory (GUSTO)
Project Title: Raising the Technology Readiness of 4.7-THz local oscillators
PI: Qing Hu (MIT)

Significance: High-reflectance UV coatings would vastly improve system throughput for photon-starved UV astronomy; this system attempted to develop advanced technique for depositing high-reflectance UV coatings
Project Title: Improving UV Coatings and Filters using Innovative Materials Deposited by ALD
PI: Paul Scowen (ASU)

Significance: Ultra-stability and -precision (~10 pm) may enable the HabEx and LUVOIR missions
Project Title: Ultra-Stable Structures
PI: Babak Saif (GSFC)